.NASA’s Record-Breaking Lucy Spacecraft Has a New Asteroid Target
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
http://jk0620.tripod.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.9
.NASA’s Record-Breaking Lucy Spacecraft Has a New Asteroid Target
NASA의 기록적인 Lucy 우주선은 새로운 소행성 목표를 가지고 있습니다
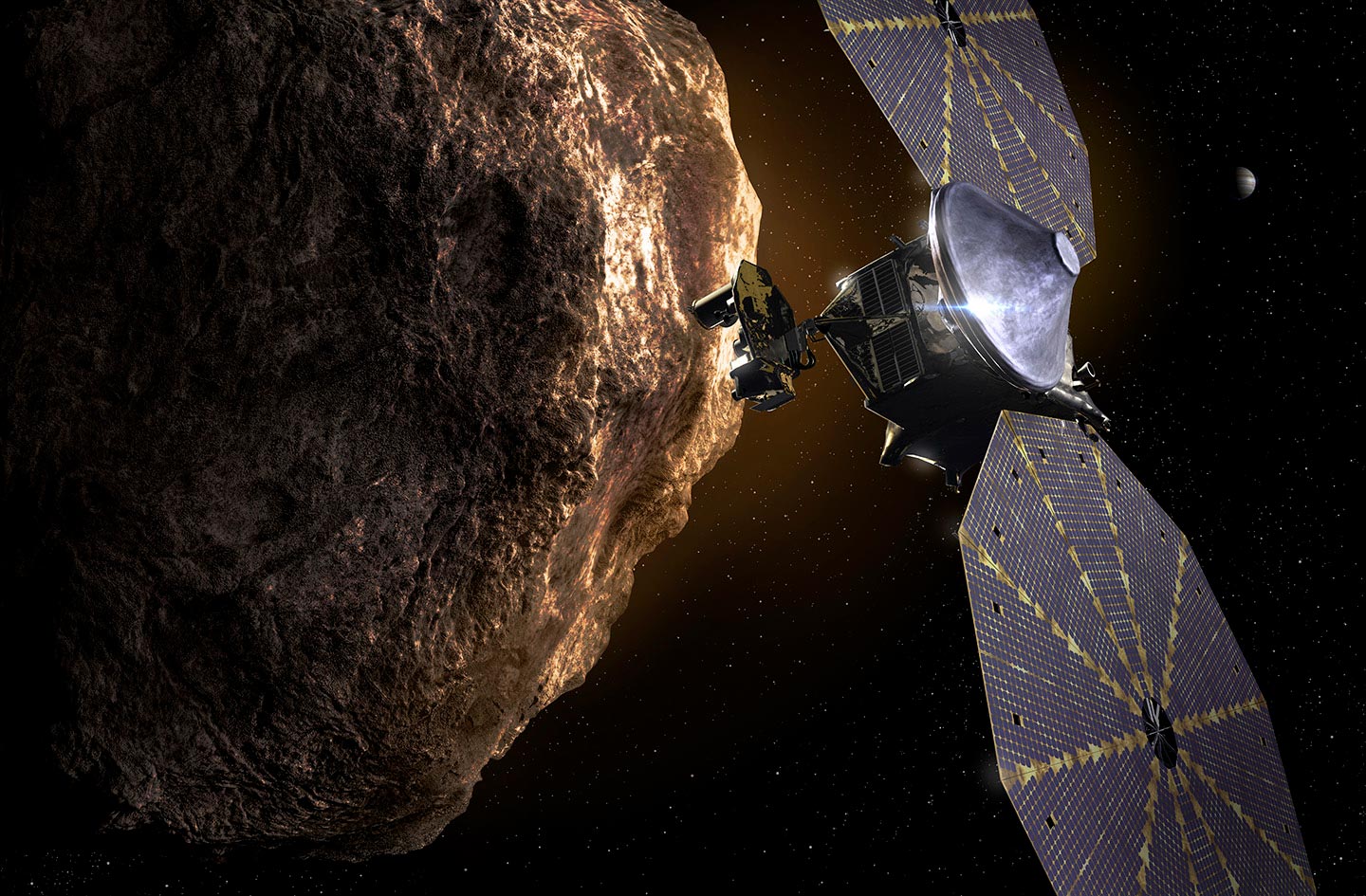

주제:소행성루시 미션NASANASA 고다드 우주 비행 센터사우스웨스트 연구소 By SOUTHWEST RESEARCH INSTITUTE 2023년 1월 30일 트로이 소행성의 루시 우주선 소행성에서 NASA의 Lucy 우주선에 대한 아티스트의 개념. 크레딧: NASA
NASA 의 루시 우주선은 40억 마일의 여정에 또 다른 소행성 만남을 추가할 것입니다. 2023년 11월 1일, Lucy는 우주선의 혁신적인 소행성 추적 내비게이션 시스템의 엔지니어링 테스트를 수행하기 위해 작은 메인 벨트 소행성을 자세히 볼 것입니다. 루시 임무는 목성 과 같은 거리에서 태양을 공전하는 목성 트로이 소행성 을 12년 동안 여행하는 동안 9개의 소행성을 방문할 계획으로 이미 기록을 깨고 있습니다 . 원래 Lucy는 메인 벨트 소행성(52246) Donaldjohanson을 지나는 2025년까지 어떤 소행성도 가까이서 볼 수 없을 예정이었습니다.
-그러나 Lucy 팀은 (152830) 1999 VD57로 지정된 내부 메인 벨트에서 아직 이름이 지정되지 않은 작은 소행성을 Lucy 우주선의 잠재적인 새롭고 유용한 목표로 식별했습니다. "주 소행성대에는 수백만 개의 소행성이 있습니다." 프랑스 니스 천문대의 루시 협력자 라파엘 마샬(Raphael Marschall)이 말했습니다. “저는 Lucy가 멀리서도 잘 볼 수 있을 만큼 충분히 가까이 이동하고 있는지 확인하기 위해 궤도가 명확한 500,000개의 소행성을 선택했습니다. 이 소행성은 정말 눈에 띄었습니다. 원래 설계된 Lucy의 궤적은 소행성에서 40,000마일 이내로 이동하며, 다음으로 가장 가까운 소행성보다 최소 3배 더 가깝습니다.” NASA Lucy 우주선 태양계 경로 NASA Lucy 우주선이 2023년 가을 주 소행성대의 안쪽 가장자리를 통과하면서 우주선은 아직 이름이 지정되지 않은 작은 소행성(152830) 1999 VD57을 지나갈 것입니다.

이 그래픽은 11월 1일 조우 직전 우주선의 궤적을 나타내는 태양계의 하향식 보기를 보여줍니다. 크레딧: NASA의 고다드 우주 비행 센터
Lucy 팀은 작은 기동을 추가하면 우주선이 이 소행성을 더 자세히 볼 수 있다는 것을 깨달았습니다. 그래서 1월 24일 팀은 우주선의 선구적인 터미널 추적 시스템의 엔지니어링 테스트로 루시의 투어에 공식적으로 추가했습니다. 이 새로운 시스템은 저공비행 임무에 대한 오랜 문제를 해결합니다. 우주선이 소행성에 접근하는 동안 우주선이 소행성에서 정확히 얼마나 떨어져 있는지, 카메라를 정확히 어느 방향으로 향해야 하는지 결정하기가 매우 어렵습니다. "과거에 대부분의 저공 비행 임무는 소행성이 있을 수 있는 지역의 이미지를 많이 촬영하여 이러한 불확실성을 설명했습니다.
-이는 효율성이 낮고 빈 공간의 이미지가 많다는 것을 의미합니다."라고 Southwest의 Lucy 수석 조사관인 Hal Levison은 말했습니다. 연구소 볼더, 콜로라도 사무실. “Lucy는 조우하는 동안 소행성을 자동으로 추적하기 위해 이 혁신적이고 복잡한 시스템을 사용하는 최초의 비행 비행 임무가 될 것입니다. 이 새로운 시스템을 통해 팀은 대상의 더 많은 이미지를 촬영할 수 있습니다.” 1999 VD57은 한 번도 비행한 적이 없는 이 절차를 검증할 수 있는 훌륭한 기회를 제공합니다. 이 조우의 기하학, 특히 우주선이 태양을 기준으로 소행성에 접근하는 각도는 임무에서 계획된 트로이 목마 소행성 조우와 매우 유사합니다. 이를 통해 팀은 우주선의 주요 과학적 목표보다 훨씬 앞서 유사한 조건에서 드레스 리허설을 수행할 수 있습니다.
이 소행성은 매우 작기 때문에 이전에 대상으로 식별되지 않았습니다. 실제로 크기가 700m에 불과한 것으로 추정되는 1999년 VD57은 우주선이 방문한 주 벨트 소행성 중 가장 작은 규모가 될 것입니다. 그것은 이전에 방문한 메인 벨트 소행성보다 최근 NASA 임무 OSIRIS-REx 및 DART 가 방문한 지구 근처 소행성과 크기가 훨씬 더 비슷합니다.
Lucy 팀은 2023년 5월 초부터 이 작은 소행성에서 약 280마일(450km) 떨어진 궤도에 우주선을 배치하기 위한 일련의 기동을 수행할 것입니다. Lucy의 수석 연구원은 텍사스주 샌안토니오에 본사를 둔 사우스웨스트 연구소 의 콜로라도주 볼더 지점에 기반을 두고 있습니다. 메릴랜드주 그린벨트에 있는 NASA의 Goddard Space Flight Center 는 전반적인 임무 관리, 시스템 엔지니어링, 안전 및 임무 보증을 제공합니다. 콜로라도 주 리틀턴에 있는 록히드 마틴 스페이스 에서 우주선을 제작했습니다. Lucy는 NASA의 디스커버리 프로그램의 13번째 임무입니다. 앨라배마 주 헌츠빌에 있는 NASA의 마샬 우주 비행 센터 는 워싱턴 에 있는 NASA 본부에서 과학 임무 위원회를 위한 발견 프로그램을 관리합니다.
https://scitechdaily.com/nasas-record-breaking-lucy-spacecraft-has-a-new-asteroid-target/
============================
메모 2301310440 나의사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
수백만 개의 소행성이 있는 소행성 벨트을 탐사선 루시가 다가가고 있다. 작은 소행성이라도 인식하려면 광시야를 가지려면 낮은 각도의 태양기준으로 소행대를 향해 접근하는 조우의 기하학이 필요할 것이다.
소행성을 자동으로 추적하기 위해 이 혁신적이고 복잡한 시스템 비행을 사용하는 것은 다목적 데이타를 얻으려는 새로운 우주 비행기술이다.
이는 마치 샘플링 oms.vix.a에 대하여 그 어떤 qoms가 접근하는 방식이다. 빈틈이 없어 보이던 샘플a.oms가 oms.vix.a.set을 이루는 모습을 보이면서 빈틈이 보이고 그곳을 향해하는 qoms.rucy가 다가가는 절묘한 순간들이다. 허허. 이는 마치 은하간 충돌에서 서로 충돌없이 빗겨가는 환상적인 시공간 조우현상이다.
Samplea.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sampleb.qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

-However, the Lucy team has identified a small as-yet-unnamed asteroid in the inner main belt, designated (152830) 1999 VD57, as a potential new and useful target for the Lucy spacecraft. “There are millions of asteroids in the main asteroid belt.” said Lucy collaborator Raphael Marschall of the Observatory in Nice, France. “I chose 500,000 asteroids with clear orbits to make sure Lucy was moving close enough to be seen well from a distance. This asteroid really stood out. Originally designed, Lucy's trajectory would travel to within 40,000 miles of the asteroid, at least three times closer than the next closest asteroid.” NASA Lucy Spacecraft Solar System Path As the NASA Lucy spacecraft passes the inner edge of the main asteroid belt in the fall of 2023, the spacecraft will pass a small as-yet-unnamed asteroid (152830) 1999 VD57.
“This means less efficiency and more empty space images,” said Hal Levison, lead investigator for Lucy at the Southwest Institute's Boulder, Colorado office. It will be the first flight mission to use the complex system, which will allow the team to take more images of the target.” The 1999 VD57 provides an excellent opportunity to validate this never-flyed procedure: the geometry of this encounter, particularly the angle at which the spacecraft approaches the asteroid relative to the sun, is very similar to the mission's planned Trojan asteroid encounter. This will allow the team to conduct dress rehearsals under similar conditions well in advance of the spacecraft's main scientific goals.
============================
memo 2301310440 my thought experiment oms storytelling
The probe Lucy is approaching an asteroid belt containing millions of asteroids. Recognition of even small asteroids would require the geometry of the encounter approaching the asteroid belt at low angles to have a wide field of view.
Using this innovative and sophisticated flying system to automatically track asteroids is a new spaceflight technique for multipurpose data acquisition.
This is how any qoms accesses sampling oms.vix.a. These are exquisite moments when the sample a.oms, which seemed to have no gaps, forms an oms.vix.a.set, and qoms.rucy, which is heading towards there, is approaching. haha. This is a fantastic space-time encounter phenomenon that misses each other without colliding with each other in a collision between galaxies.
Samplea.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sampleb. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

.Surprising Discovery: Graphene on Platinum Surfaces Seemingly Defies Coulomb’s Law
놀라운 발견: 백금 표면의 그래핀은 쿨롱의 법칙을 무시하는 것처럼 보입니다
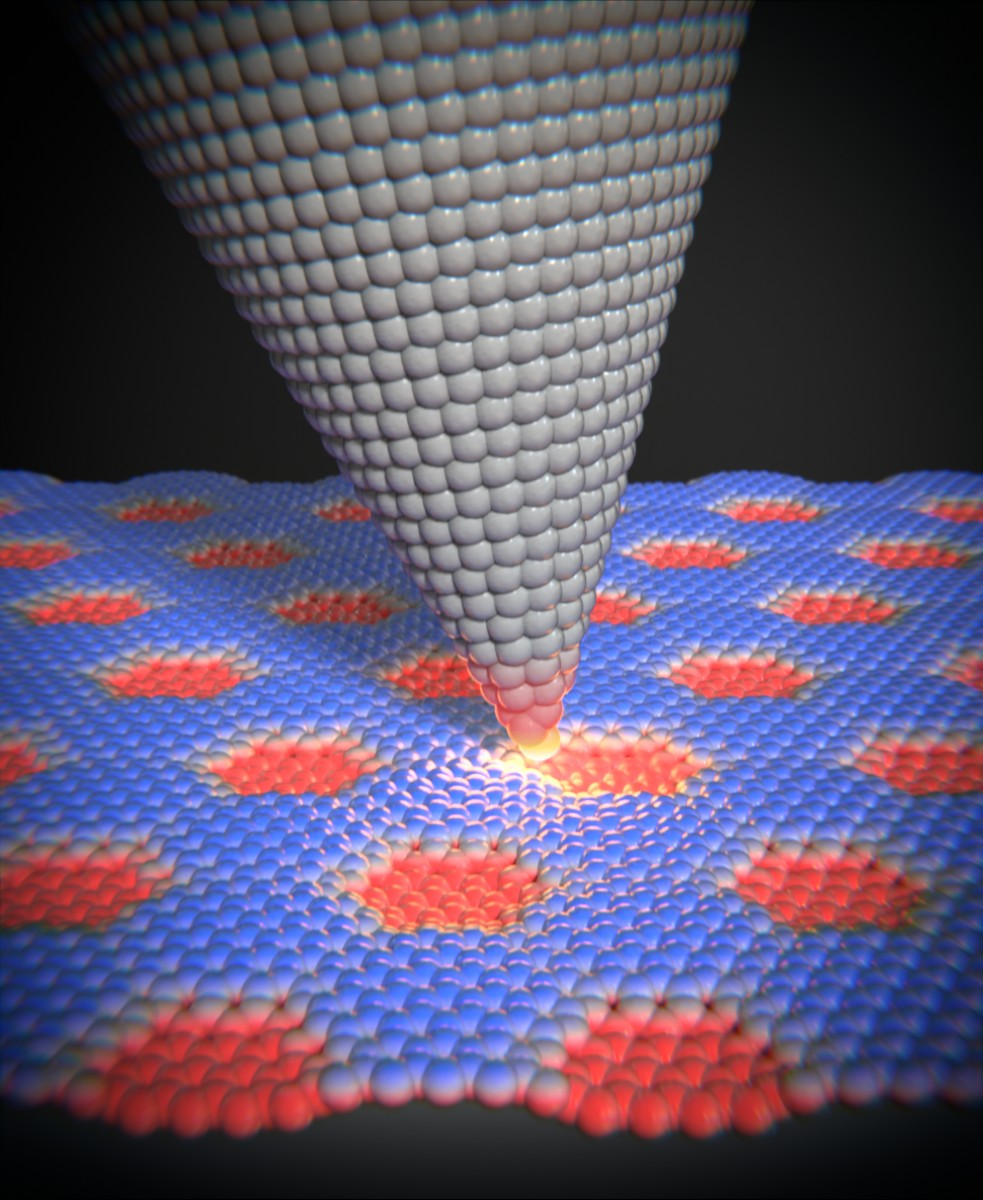
주제:마찰그래핀텔아비브대학교바젤 대학교 스위스 나노과학 연구소, 바젤 대학교 2023년 1월 30 일 속도 종속 마찰 놀랍게도 원자간력 현미경의 팁과 Moiré 상부 구조 사이의 마찰은 팁이 표면을 가로질러 이동하는 속도에 따라 달라집니다. 학점: University of Basel and Scixel JANUARY 30, 2023
-물리학과 바젤과 텔아비브의 연구원들은 백금 표면의 특정 그래핀 구조에서 마찰이 속도에 따라 달라지는 것을 발견했으며, 이는 매크로 세계에서 마찰이 속도와 무관하다는 쿨롱의 법칙을 무시하는 것입니다. 단일 원자층으로 만들어진 재료는 저마찰 특성으로 높은 평가를 받고 있으며, 하드 디스크나 위성 또는 우주 망원경의 움직이는 부품의 마찰을 줄이는 데 유용합니다.
-벌집 모양으로 배열된 탄소 원자의 단일 층으로 구성된 그래핀이 대표적인 예이며 윤활층으로서의 가능성을 검토하고 있습니다. 이전 연구에서는 그래핀 리본이 금 표면에서 거의 마찰 없이 미끄러질 수 있음을 보여주었습니다. 거친 표면의 놀라운 결과 그래핀을 백금 표면에 적용하면 측정 가능한 마찰력에 상당한 영향을 미칩니다. 이제 바젤 대학 과 텔아비브 대학 의 물리학자들은 나노 레터스 저널 에 이 경우 마찰은 원자력 현미경(AFM; 상자 참조)의 팁이 표면을 가로질러 움직이는 속도에 따라 달라진다고 보고했습니다.
-표면. 매크로 세계에 적용되는 쿨롱의 법칙에 따르면 마찰은 속도에 의존하지 않기 때문에 이 발견은 놀라운 것입니다. 백금 기판과 함께 그래핀은 더 이상 탄소 원자의 육각형 벌집 패턴만 형성하지 않고 대신 모아레 초격자로 알려진 상부 구조를 형성합니다. 그러면 표면이 더 이상 완전히 평평하지 않고 어느 정도 거칠어집니다.
-스위스 나노과학 연구소(Swiss Nanoscience Institute)와 바젤 대학 물리학과의 Ernst Meyer 교수는 “저속으로 이 약간 주름진 표면을 가로질러 AFM 팁을 움직이면 약하고 거의 일정한 마찰력을 측정합니다. "그러나 특정 임계값 이상에서 마찰은 AFM 팁의 속도와 함께 증가합니다."라고 제1저자 Dr. Yiming Song이 덧붙였습니다. "모아레 상부 구조가 클수록 마찰이 속도에 따라 달라지는 임계값이 낮아집니다." 연구원들은 팁이 움직이는 동안 Moiré 상부 구조의 능선에서 더 큰 저항이 있음을 발견했습니다. 이 릿지는 압력이 충분히 높을 때 다시 이완되기 전에 푸싱 팁으로 인해 탄성 변형을 겪습니다. 이 효과는 팁의 속도에 따라 증가하는 더 큰 마찰력을 초래합니다. 시뮬레이션 및 분석 모델은 이 국제 연구팀이 얻은 실험 결과를 확인합니다.
참조: Yiming Song, Xiang Gao, Antoine Hinaut, Sebastian Scherb, Shuyu Huang, Thilo Glatzel, Oded Hod, Michael Urbakh 및 Ernst Meyer의 "모아레 마찰의 속도 의존성", Nano Letters. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c03667
============================
메모 2301310524 나의사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
초격자 탄소나노튜브 그래핀을 모아레 패턴으로 샘플링 poms를 쌓아 올리면 소수는 표면에서 속도와 무관하게 슬며시 빠져 나간다. 이는 표면적 매크로 세계에 적용되는 쿨롱의 법칙에 따르면 마찰은 속도에 의존하지 않기 때문에 이 발견은 놀라운 것이다.
만약에 초거대 소수가 poms의 모드로 나타나 단하나의 입자에 의해 성립되지 않는다면 그 작은 마찰력으로 인하여 속도와 관련없이 뒤엉키는 상태가 나타난다. 우주에서 은하간 충돌로 살아남는 구역이 존재한다면 아마 poms가 qoms를 통과될 것이고 그렇지 않다면 banqing 여닫이 격자에 따라 속도에 따른 마찰 충돌이 다양하게 생겨날 것이다.
Samplea.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sampleb.qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

- Physics and researchers in Basel and Tel Aviv have found that friction varies with speed in certain graphene structures on platinum surfaces, defying Coulomb's law, which states that friction is speed independent in the macro world. Materials made of single atomic layers are highly valued for their low friction properties and are useful for reducing friction in hard disks or moving parts of satellites or space telescopes.
-Graphene composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb is a typical example, and its potential as a lubricating layer is being reviewed. Previous studies have shown that graphene ribbons can slide almost frictionlessly on a gold surface. Surprising results on rough surfaces Applying graphene to a platinum surface has a significant impact on measurable frictional forces. Now, physicists from the University of Basel and Tel Aviv University report in the journal Nano Letters that the friction in this case depends on the speed at which the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM; see box) moves across a surface.
-surface. This discovery is surprising because according to Coulomb's law, which applies to the macro world, friction does not depend on speed. Together with a platinum substrate, graphene no longer forms just a hexagonal honeycomb pattern of carbon atoms, but instead forms a superstructure known as a moiré superlattice. The surface will then no longer be completely flat and will be somewhat rough.
-Professor Ernst Meyer from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel explains: “Moving the AFM tip across this slightly corrugated surface at low speed measures a weak, almost constant frictional force. "But above a certain threshold, friction increases with the speed of the AFM tip," said first author Dr. Yiming Song added, “The larger the moiré superstructure, the lower the threshold at which friction becomes velocity dependent.” The researchers found that there was greater resistance at the ridges of the Moiré superstructure while the tip moved. This ridge undergoes elastic deformation due to the pushing tip before relaxing again when the pressure is high enough. This effect results in a greater frictional force that increases with the speed of the tip. Simulation and analytical models confirm the experimental results obtained by this international research team.
============================
memo 2301310524 my thought experiment oms storytelling
When sampling poms of superlattice carbon nanotube graphene are piled up in a moiré pattern, the prime numbers slip away from the surface regardless of speed. This discovery is surprising because, according to Coulomb's law, which applies to the surface macro world, friction does not depend on speed.
If a super-majority prime appears in the mode of poms and is not established by a single particle, the small frictional force causes an entangled state regardless of speed. If there are regions in the universe that survive intergalactic collisions, poms will probably pass through qoms, otherwise frictional collisions will vary with velocity depending on the banqing casement grid.
Samplea.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sampleb. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca
댓글