.Hubble captures rare 'light echo' from star explosion
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
http://jk0620.tripod.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.9
.Are Newton’s Laws of Gravity Wrong: Observation Puzzles Researchers
뉴턴의 중력 법칙이 잘못된 것인가: 관찰 퍼즐

연구자 주제:천체물리학중력본 대학교 본 대학교 2022년 10월 29 일 깨진 중력 개념 OCTOBER 29, 2022
천체 물리학자들은 특정 성단을 분석하는 동안 수수께끼 같은 발견을 했습니다. 이 발견은 뉴턴의 중력 법칙에 도전합니다. 대신, 관측 결과는 대체 중력 이론의 예측과 일치합니다. (기묘한 중력의 예술적 개념.) 발견은 고전적인 가정으로 설명할 수 없습니다. 천체 물리학자로 구성된 국제 팀이 특정 성단을 분석하는 동안 수수께끼 같은 발견을 했습니다. 이 발견은 뉴턴의 중력 법칙에 도전한다고 연구원들은 그들의 간행물에 씁니다. 대신, 관측 결과는 대체 중력 이론의 예측과 일치합니다. 그러나 이는 전문가들 사이에서 논란이 되고 있다.
그 결과는 현재 왕립천문학회의 월간통지(Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society)에 실렸다. 본 대학은 이 연구에서 중요한 역할을 했습니다. 그들의 작업에서 연구원들은 나선 은하와 불규칙 은하에서 발견되는 수십에서 수백 개의 별이 느슨하게 묶인 그룹인 산개 성단을 조사했습니다. 산개성단은 거대한 가스 구름 속에서 수천 개의 별이 짧은 시간 안에 태어날 때 형성됩니다. 그들이 "발화"하면서 은하계의 새로운 이민자들은 가스 구름의 잔해를 날려 버립니다. 그 과정에서 클러스터가 크게 확장됩니다.

이것은 수십에서 수천 개의 별의 느슨한 형성을 만듭니다. 클러스터는 그들 사이에 작용하는 약한 중력에 의해 함께 유지됩니다. 본 대학 헬름홀츠 방사선 및 핵물리학 연구소의 파벨 크루파(Pavel Kroupa) 교수는 “대부분의 경우 산개성단은 몇 억 년 동안만 살아남은 채 분해되지 않는다”고 설명합니다. 그 과정에서 그들은 정기적으로 별을 잃어버리고 두 개의 소위 "조석 꼬리"에 축적됩니다. 이 꼬리 중 하나는 우주를 여행할 때 클러스터 뒤로 당겨집니다. 이에 반해 다른 하나는 선봉장처럼 앞장서고 있다.
파벨 크루파 본 대학 헬름홀츠 방사선 및 핵 물리학 연구소의 파벨 크루파(Pavel Kroupa) 교수. 크레딧: Volker Lannert / 본 대학교 "뉴턴의 중력 법칙에 따르면 잃어버린 별의 꼬리 중 어느 쪽이 끝나는지는 우연의 문제입니다."라고 Helmholtz Institute of Radiation and Nuclear Physics의 Jan Pflamm-Altenburg 박사가 설명합니다. “따라서 양쪽 꼬리에는 거의 같은 수의 별이 있어야 합니다. 그러나 우리 연구에서 이것이 사실이 아님을 처음으로 증명할 수 있었습니다. 우리가 연구한 성단에서 앞 꼬리에는 항상 뒷 꼬리보다 성단 근처에 훨씬 더 많은 별이 포함되어 있습니다.” 별을 세기 위해 개발된 새로운 방법 성단에 가까운 수백만 개의 별 중에서 지금까지는 꼬리에 속하는 별을 판별하는 것이 거의 불가능했습니다. 테레자 제라브코바 박사는 “이렇게 하려면 각 물체의 속도, 운동 방향, 나이를 살펴봐야 합니다. Kroupa의 그룹에서 박사 학위를 취득한 논문의 공동 저자는 최근 유럽 우주국(ESA) 에서 Garching의 유럽 남방 천문대로 옮겼습니다. 그녀는 처음으로 꼬리에 있는 별을 정확하게 셀 수 있는 방법을 개발했습니다. "지금까지 우리가 4개를 포함하여 우리 근처에서 5개의 열린 클러스터를 조사했습니다."라고 그녀는 말합니다. “모든 데이터를 분석했을 때 현재 이론과 모순되는 부분에 직면했습니다. ESA의 Gaia 우주 임무 에서 얻은 매우 정확한 측량 데이터이를 위해 없어서는 안 될 존재였습니다.”
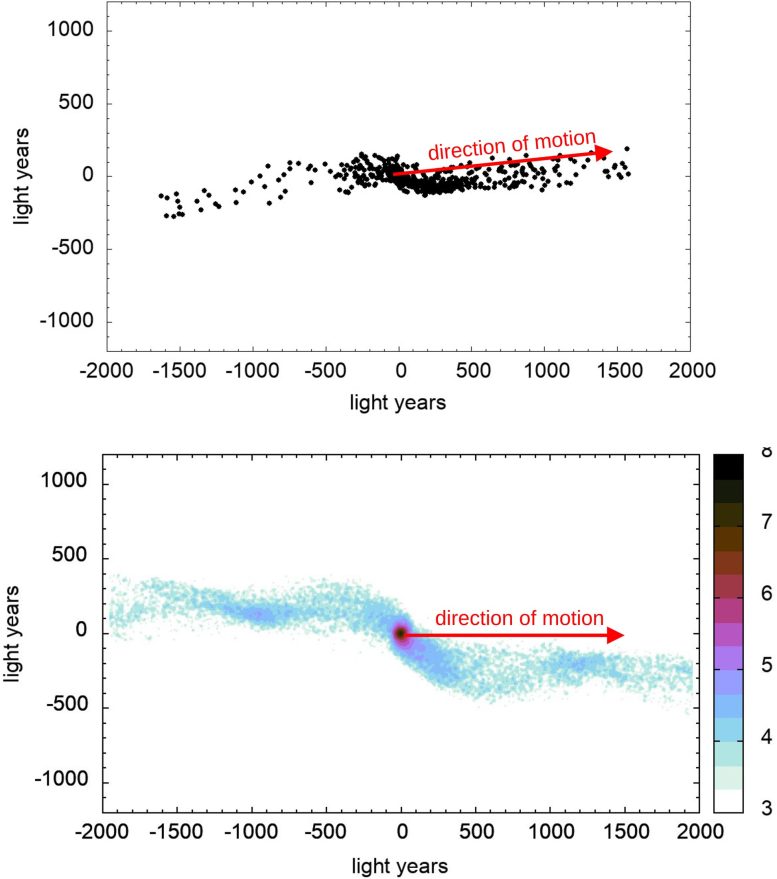
Hyades 성단 앞바다 이야기 성단 "Hyades"(위)에서 앞쪽 조석 꼬리에 있는 별(검정색)의 수는 뒤쪽에 있는 것보다 훨씬 많습니다. MOND를 사용한 컴퓨터 시뮬레이션(아래)에서도 비슷한 그림이 나타납니다. 크레딧: AG Kroupa/Uni Bonn
대조적으로, 관측 데이터는 전문가들 사이에서 약어 MOND ("수정된 뉴턴 역학") 로 가는 이론과 훨씬 더 잘 맞습니다 . "간단히 말해서 MOND에 따르면 별은 두 개의 다른 문을 통해 성단을 떠날 수 있습니다."라고 Kroupa는 설명합니다. “하나는 뒤쪽 조석 꼬리로, 다른 하나는 앞쪽으로 연결됩니다. 그러나 첫 번째는 두 번째 것보다 훨씬 좁기 때문에 별이 그것을 통해 성단을 떠날 가능성이 적습니다. 반면에 뉴턴의 중력 이론은 두 문이 같은 너비여야 한다고 예측합니다.” 성단은 뉴턴의 법칙이 예측하는 것보다 수명이 짧습니다. 천체 물리학자 팀은 MOND에 따라 예상되는 항성 분포를 계산했습니다. 해당 시뮬레이션에서 핵심 역할을 한 Ingo Thies 박사는 "결과는 관찰 결과와 놀라울 정도로 잘 일치합니다."라고 강조합니다.
“그러나 우리는 이를 수행하기 위해 비교적 간단한 계산 방법에 의존해야 했습니다. 우리는 현재 수정된 뉴턴 역학의 보다 상세한 분석을 위한 수학적 도구가 부족합니다.” 그럼에도 불구하고 시뮬레이션은 또 다른 측면에서 관찰과 일치했습니다. 그들은 열린 성단이 일반적으로 얼마나 오래 생존해야 하는지를 예측했습니다. 그리고 이 시간 범위는 뉴턴의 법칙에 따라 예상되는 것보다 훨씬 짧습니다. Kroupa는 "이것은 오랫동안 알려진 미스터리를 설명합니다."라고 지적합니다. "즉, 가까운 은하에 있는 성단이 생각보다 빨리 사라지고 있는 것 같습니다."
그러나 MOND 이론은 전문가들 사이에서 논란의 여지가 없습니다. 뉴턴의 중력 법칙은 특정 상황에서는 유효하지 않지만 수정되어야 하기 때문에 다른 물리학 분야에도 광범위한 영향을 미칠 것입니다. 본 대학의 "모델링" 및 "물질" 분야 초학문 연구 분야의 일원이기도 한 Kroupa는 "다시 말하지만, 그것은 오늘날 우주론이 직면한 많은 문제를 해결합니다."라고 설명합니다. 천체 물리학자들은 이제 훨씬 더 정확한 시뮬레이션을 위한 새로운 수학적 방법을 탐구하고 있습니다. 그런 다음 MOND 이론이 올바른지 아닌지에 대한 추가 증거를 찾는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
참조: Pavel Kroupa, Teresa Jerabkova, Ingo Thies, Jan Pflamm-Altenburg, Benoit Famaey, Henri MJ Boffin, Jörg Dabringhausen, Giacomo Beccari, Timo Prusti, Hosein Haghi, Xufen Wu, Jaroslav Haas, Akram Hasani Zonoozi, Guillaume Thomas, Ladislav Shubr 및 Sverre J Aarseth, 2022년 10월 26일, Royal Astronomical Society 의 월간 공지 DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stac2563 본 대학 외에도 이 연구에는 프라하의 카를 대학, 가르칭의 유럽 남방 천문대( ESO ), 스트라스부르 천문대, Nordwijk의 유럽 우주 연구 및 기술 센터(ESA ESTEC), 잔잔(이란)의 기초 과학 고급 연구(IASBS), 중국 과학 기술 대학교, 테네리페의 라 라구나 대학교, 케임브리지 대학교. 이 연구는 체코 공화국의 장학금 프로그램, 독일 학술 교류 서비스(DAAD), 프랑스 자금 지원 기관인 ANR(Agence nationale de la recherche) 및 유럽 연구 위원회 ERC의 지원을 받았습니다.
https://scitechdaily.com/are-newtons-laws-of-gravity-wrong-observation-puzzles-researchers/

.Hubble captures rare 'light echo' from star explosion
허블, 별 폭발에서 드문 '빛의 메아리' 포착
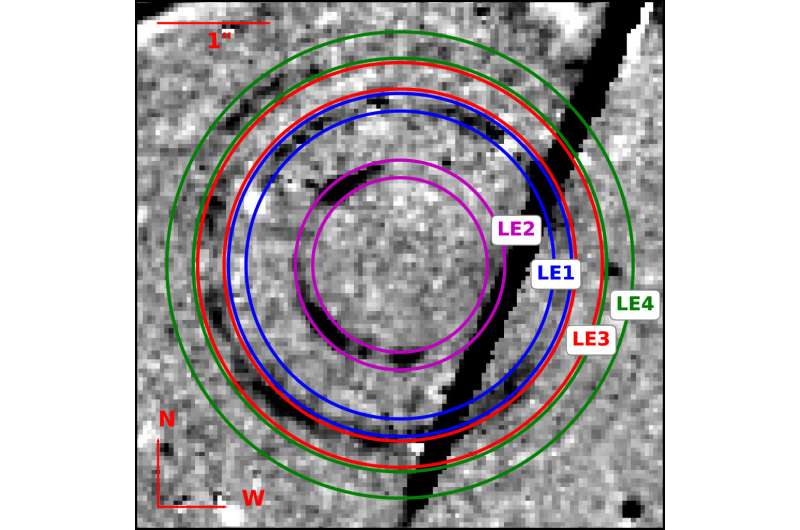
유니버시티 칼리지 더블린 +1991일에 SN 2016adj의 호스트 빼기 F555W 밴드 HST 이미지, LE1, LE2, LE3 및 LE4의 위치는 색상 링으로 강조 표시되고 레이블이 지정됩니다. 크레딧: The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2022). https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac93f8 OCTOBER 28, 2022
별이 폭발할 때(초신성), 강렬한 빛의 폭발을 모든 방향으로 보냅니다. 드문 경우지만 그 후 몇 달과 몇 년 동안 빛의 고리 또는 "빛의 메아리"가 원래의 초신성 위치에서 퍼집니다. 이것은 더블린, 바르셀로나, 오르후스, 뉴욕 및 가칭의 천문학자들이 공동으로 수행한 허블 우주 망원경(HST) 관측을 기반으로 한 천체 물리학 저널 레터( The Astrophysical Journal Letters )의 최근 논문에서 설명한 내용입니다. "허블 우주 망원경이 센타우루스 A의 상징적인 먼지 차선에 있는 벗겨진 외피 초신성 2016adj와 관련된 장엄한 빛의 메아리를 보여줍니다"라는 논문이 이번 주에 발표되었습니다. 과학자들은 HST 이미지를 짧은 gif 비디오로 병합하여 맨 처음 초신성 폭발을 처음으로 중심에서 보여주고 폭발로 인한 빛이 주변의 다양한 먼지 층에 부딪힐 때 나타나는 빛 고리를 보여줍니다.
크레딧: 유니버시티 칼리지 더블린
덴마크 오르후스 대학의 수석 과학자인 Maximillian Stritzinger 교수는 "데이터 세트는 놀랍고 우리가 5년 동안 빛 에코의 진화를 보여주는 매우 인상적인 컬러 이미지와 애니메이션을 생성할 수 있게 해주었다. 이전에는 소수의 다른 초신성에서만 기록된 현상입니다." 공동 저자이자 더블린에 기반을 둔 천체 물리학자인 UCD 물리학 대학의 Dr. Morgan Fraser는 "James Webb Space Telescope가 많은 관심을 끌었지만, 그 전신인 Hubble은 계속해서 놀라운 우주 이미지를 제공하고 있습니다.
HST는 이제 우주를 관측하고 있습니다. 30년 이상 동안 하늘을 관찰한 결과, 수년에 걸쳐 천천히 진화하는 이 빛의 메아리 와 같은 것을 찾을 수 있습니다 ." 공동 저자인 바르셀로나 우주 과학 연구소(Institute of Space Sciences)의 Dr. Lluis Galbany는 "이 강력한 초신성 폭발 의 폭발파는 초당 10,000km가 넘는 속도로 바깥쪽으로 질주하고 있습니다. 이 폭발파 앞에는 초신성에서 방출되는 강렬한 빛의 섬광이 있습니다. 그리고 이것이 우리가 이미지에서 볼 수 있는 팽창하는 고리를 일으키는 원인입니다.
-초신성은 이러한 우주 폭발이 우리 은하, 별 및 행성을 구성하는 탄소, 산소 및 철과 같은 많은 무거운 원소 를 생성하기 때문에 관심이 있습니다. " 공동 저자인 뉴욕 호프스트라 대학교(Hofstra University)의 스티븐 로렌스(Stephen Lawrence) 박사는 다음과 같이 말했습니다. 그 지역에 아직 남아 있는 초기 포탄에서 몇 분에 걸쳐 촬영한 일련의 사진을 비교함으로써 장면을 밝히고 있는 가장 최근의 폭발과 직접 관련이 없는 모든 종류의 정보를 측정할 수 있습니다.
포탄이 이전에 폭발한 적이 있는지, 주어진 포탄에서 나오는 연기가 얼마나 불투명한지, 바람이 얼마나 빠르고 어떤 방향으로 부는지 등입니다." SN 2016adj로 명명된 문제의 초신성은 2016년에 처음 발견되었으며 지구에서 1000만~1600만 광년 거리에 위치한 잘 알려진 독특한 은하인 Centaurus A에 속합니다. 5년 반 동안 천문학자들은 초신성이 서서히 사라지는 주변 지역을 관찰했습니다.
-Centaurus A는 먼지 차선으로 가득 차 있으며 시간이 지남에 따라 초신성에서 옆으로 퍼지는 빛이 먼지가 많은 지역에 부딪치면 원래 초신성 위치에서 점점 더 멀어져 빛의 에코라고 불리는 일련의 팽창하는 방출 고리를 만듭니다.
관찰 기간 동안 이러한 고리의 변화는 연구원들이 폭발 근처에 있는 은하의 먼지 차선의 배치를 조사할 수 있게 해줍니다. 데이터는 그것들이 스위스 치즈 덩어리를 닮은, 그 사이에 큰 구멍이 있는 먼지 기둥으로 구성되어 있음을 시사합니다. Stritzinger 교수는 "Centaurus A는 거대한 타원은하입니다. 이들은 대부분 조용하고 먼지가 없으며 초신성으로 폭발하는 경향이 있는 젊은 별이 없습니다. 그러나 Centaurus A는 분명히 다릅니다.
-강력한 방사성천문학 소스이며 눈에 띄는 먼지 띠를 포함하고 있습니다." 내부에서 새로운 별이 형성되고 있습니다. 이것은 '최근에' 또 다른 작은 나선 은하를 집어삼켰으며, 문제는 수억 년 동안처럼 아직 해결되지 않았다는 신호입니다.
-메아리는 우리가 이 격렬한 은하 충돌에 대한 더 많은 통찰력을 얻는 데 도움이 될 것입니다." 지금까지 4개의 서로 다른 먼지 시트에 의해 생성된 4개의 뚜렷한 빛 에코가 관찰되었습니다. SN 2016adj에 대한 데이터 세트는 초신성과 관련된 빛 반향 방출의 가장 빠른 탐지를 제공합니다. 팀은 이러한 방출을 별이 폭발한 지 50일 전에 측정할 수 있었지만 SN 2014J와 같은 HST가 포착한 이전의 빛 반향은 폭발이 일어난 지 수백 일 전에 시작되었습니다. 또한 이것은 Ic형 초신성 주변에서 발견된 최초의 빛 에코입니다. 독일 가르칭(Garching)에 있는 유럽 남방 천문대(European Southern Observatory)의 페르디난도 파타트(Ferdinando Patat) 박사가 포함된 팀은 앞으로 더 많은 빛 고리가 나타나기를 희망하면서 HST로 관측을 추적할 계획입니다. 더욱이, 빛 에코의 스펙트럼을 얻는 것이 가능할 수 있으며, 이는 실제로 밑에 있는 초신성의 스펙트럼을 보여줍니다.
추가 탐색 이미지: 허블은 폭발적인 과거를 가진 은하를 본다 추가 정보: Maximilian D. Stritzinger et al, Hubble Space Telescope Reveals Spectacular Light Echoes Associated with Stripped-envelope Supernova 2016adj in the Iconic Dust Lane of Centaurus A, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2022). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac93f8 . iopscience.iop.org/article/10. … 847/2041-8213/ac93f8 저널 정보: 천체물리학 저널 레터 유니버시티 칼리지 더블린 제공
https://phys.org/news/2022-10-hubble-captures-rare-echo-star.html
==========================
메모 2210300119 나의 사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
허블, 별 폭발에서 드문 '빛의 메아리' 포착했다. 소리가 메아리를 나타내듯 샘플c.oss의 확장성 에고 빛의 파장은 초신성의 지문이 될 수 있다. 이는 태양이 방사선 방출의 나이테를 가지는 연구보고와 일련의 공통적 에코.나이테 지문발생 연관성을 암시한다.
초신성의 폭발적인 포탄이나 태양의 지속적인 방사선 방출은 샘플c.oss의 단계적 에코 지문 현상을 닮았다. 그 차이는 oss.base.feedback은 결코 사라지는 것이 아닌 더 확장된 무한 질량이고 부피이다.
샘플a.oms(standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플b.qoms(standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
샘플b.poms(standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
샘플c.oss(standard)zxdxybzyz
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

-Centaurus A is filled with dust lanes, and over time, as light beaming from a supernova laterally hits a dusty region, it moves further and further away from its original supernova location, creating a series of expanding rings of emission called echoes of light.
Changes in these rings during observations allow researchers to investigate the arrangement of dust lanes in galaxies near the explosion. Data suggest they consist of pillars of dust with large holes in between, resembling chunks of Swiss cheese. "Centaurus A is a huge elliptical galaxy," said Professor Stitzinger. "They are mostly quiet, dusty, and do not have young stars that tend to explode as supernovae. But Centaurus A is clearly different."
-It is a powerful radioastronomical source and contains prominent dust bands." Inside, new stars are forming. This has 'recently' swallowed up another small spiral galaxy, and the problem has not been resolved as it has been for hundreds of millions of years. This is a signal that it didn't.
-Echoes will help us gain more insight into this violent galactic collision." So far, four distinct light echoes produced by four different dust sheets have been observed. Data for SN 2016adj The set provides the fastest detection of light echo emissions associated with supernovae, where the team was able to measure these emissions 50 days before the star exploded, but previous light echoes captured by HSTs, such as SN 2014J, were able to determine if the explosion occurred. It started hundreds of days ago.It is also the first light echo to be found around a Type Ic supernova.A team including Dr. Ferdinando Patat of the European Southern Observatory in Garching, Germany plans to track observations with HST in the hopes that more light rings will appear in the future.Moreover, it may be possible to obtain spectra of light echoes, which actually show the spectrum of the underlying supernova.
============================
Memo 2210300119 My Thought Experiment oms Storytelling
Hubble catches rare 'echoes of light' in star explosions As a sound represents an echo, the wavelength of the expanding ego light of sample c.oss could be the fingerprint of a supernova. This suggests a set of common echo.ringe fingerprinting associations with studies reporting that the sun has radiated ring rings.
The explosive shells of a supernova or the continuous emission of radiation from the sun resembles the phenomenon of a gradual echo fingerprint of sample c.oss. The difference is that oss.base.feedback never disappears, but a more extended infinite mass and volume.
Sample a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample b.qoms(standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms(standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss(standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

.Tree Rings Offer Insight Into Mysterious, Devastating Radiation Storms
나무 고리는 신비하고 파괴적인 방사선 폭풍에 대한 통찰력을 제공합니다

주제:태양 플레어우주 날씨퀸즐랜드 대학교 2022년 10월 28일 퀸즐랜드 대학교 나이테와 태양 나무 나이테와 불꽃을 보여주는 합성 이미지 – UQ 연구원은 나무 나이테 데이터를 사용하여 Miyake 이벤트에 대한 일반적인 이론에 도전하기 위해 전지구 탄소 순환을 모델링했습니다. 크레딧: 퀸즐랜드 대학교
-퀸즐랜드 대학(UQ)의 연구 덕분에 신비하고 예측할 수 없으며 잠재적으로 파괴적인 천체 물리학 사건에 대한 새로운 시각이 밝혀졌습니다. UQ 수학 및 물리학 학교의 Benjamin Pope 박사가 이끄는 연구원 팀은 방사선 '폭풍'에 대해 자세히 알아보기 위해 수천 년 된 나무의 데이터에 최첨단 통계를 적용했습니다. "미야케 사건으로 알려진 이 거대한 우주 방사선 폭발은 대략 천 년에 한 번 발생했지만 원인이 불분명합니다."라고 포프 박사는 말했습니다.
“주요 이론은 그것들이 거대한 태양 플레어라는 것입니다. 오늘날 이 중 하나가 발생하면 위성, 인터넷 케이블, 장거리 전력선 및 변압기를 포함한 기술이 파괴될 것이기 때문에 우리는 더 많이 알아야 합니다. "글로벌 인프라에 미치는 영향은 상상할 수 없을 것입니다." "단일의 순간적인 폭발이나 플레어가 아니라 우리가 보고 있는 것은 일종의 천체 물리학 '폭풍' 또는 폭발입니다." — 장칭위안 겸손한 나이테를 입력하십시오.
-제1저자인 UQ 학부 수학 학생인 Qingyuan Zhang은 나이테에 대한 모든 사용 가능한 데이터를 분석하는 소프트웨어를 개발했습니다. Zhang은 "나무의 고리를 세어 나이를 식별할 수 있기 때문에 수천 년 전으로 거슬러 올라가는 역사적 우주 사건을 관찰할 수도 있습니다."라고 말했습니다. “방사선이 대기에 부딪히면 방사성 탄소-14가 생성되며, 이는 공기, 바다, 식물 및 동물을 통해 여과되고 나이테에 연간 방사선 기록을 생성합니다. "우리는 Miyake 이벤트의 규모와 성격에 대한 통찰력을 얻기 위해 10,000년 동안 프로세스를 재구성하기 위해 글로벌 탄소 순환을 모델링했습니다."
지금까지의 일반적인 이론은 미야케 사건이 거대한 태양 플레어라는 것이었습니다. "그러나 우리의 결과는 이것에 도전합니다"라고 Zhang은 말했습니다. “우리는 그것들이 흑점 활동과 상관관계가 없다는 것을 보여주었고 일부는 실제로 1~2년 동안 지속되었습니다. "단일의 순간적인 폭발이나 플레어가 아니라 우리가 보고 있는 것은 일종의 천체 물리학 '폭풍' 또는 폭발입니다." "글로벌 인프라에 미치는 영향은 상상할 수 없을 것입니다." — 벤자민 포프 박사 포프 박사는 과학자들이 미야케 사건이 무엇인지 정확히 알지 못하거나 그 발생을 예측하는 방법을 모른다는 사실이 매우 혼란스럽다고 말했습니다.
“이용 가능한 데이터에 따르면 향후 10년 이내에 다른 데이터를 볼 확률이 대략 1%입니다. 그러나 우리는 그것을 예측하는 방법이나 그것이 초래할 수 있는 피해를 모릅니다. "이러한 확률은 매우 놀랍고 추가 연구를 위한 토대를 마련합니다." 이 연구는 왕립학회 회보 A에 게재되었습니다 . 참조: Qingyuan Zhang, Utkarsh Sharma, Jordan A. Dennis, Andrea Scifo, Margot Kuitems, Ulf Büntgen, Mathew J. Owens, Michael W. Dee 및 Benjamin JS Pope의 "모델링 cosmic radiation events in tree-ring radiocarbon record" , 왕립 학회 A 수리 물리 및 공학 과학의 회보 . DOI: 10.1098/rspa.2022.0497 이 연구는 또한 학부 수학 및 물리학 학생인 Utkarsh Sharma와 Jordan Dennis와 함께 완료되었습니다. 이 작업은 Big Questions Institut에서 UQ에 대한 자선 기부로 지원되었습니다.
https://scitechdaily.com/tree-rings-offer-insight-into-mysterious-devastating-radiation-storms/
=========================
메모 2210300119 나의 사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
허블, 별 폭발에서 드문 '빛의 메아리' 포착했다. 소리가 메아리를 나타내듯 샘플c.oss의 확장성 에고 빛의 파장은 초신성의 지문이 될 수 있다. 이는 태양이 방사선 방출의 나이테를 가지는 연구보고와 일련의 공통적 에코.나이테 지문발생 연관성을 암시한다.
"미야케 사건으로 알려진 태양의 이 거대한 우주 방사선 폭발은 대략 천 년에 한 번 발생했지만 원인이 불분명하다." 태양 폭풍은 지구 상층 대기에 많은 우주선을 방출하기 때문에 탄소 방사성 동위 원소인 탄소14를 생성한다. 따라서 오랜 세월에 거쳐 쌓인 남극 얼음에 포함된 탄소14 층과 함량으로부터 과거 언제쯤 태양 폭풍(oss.base) 초기값이 발생했는지를 알 수 있다. 허허.
우주에는 수많은 별들이 존재하고 그곳에서 발생하는 자기폭풍들이 oss.base.initial values들이 항성간의 광자, 전자기장.중력장의 메아리 메세지 파문으로 상호작용하는듯 하다. 허허.
샘플a.oms(standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플b.qoms(standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
샘플b.poms(standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
샘플c.oss(standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

- Research at the University of Queensland (UQ) has revealed new perspectives on mysterious, unpredictable and potentially devastating astrophysical events. A team of researchers led by Dr. Benjamin Pope at the UQ School of Mathematics and Physics applied state-of-the-art statistics to data from thousands of years old trees to learn more about the radiation 'storm'. "This massive explosion of cosmic radiation, known as the Miyake Incident, occurred about once in a thousand years, but the cause is unclear," said Dr. Pope.
“The main theory is that they are huge solar flares. We need to know more today because if any of these happens today, technology will be disrupted, including satellites, internet cables, long-distance power lines, and transformers. “The impact on the global infrastructure is unimaginable.” "What we're seeing is not a single instantaneous explosion or flare, but some sort of astrophysical 'storm' or explosion." — Enter the Zhang Qingyuan modest ring.
-The first author, Qingyuan Zhang, a UQ undergraduate mathematics student, developed a software that analyzes all available data on tree rings. "Because you can identify the age by counting the rings on a tree, you can also observe historical cosmic events that go back thousands of years," Zhang said. “When radiation hits the atmosphere, it produces radioactive carbon-14, which is filtered through the air, sea, plants and animals and creates annual radiographic records in the tree rings. “We modeled the global carbon cycle to reconstruct processes over 10,000 years to gain insight into the scale and nature of the Miyake event.”
Material 1.
Solar storms release many cosmic rays into Earth's upper atmosphere, producing carbon 14, a carbon radioactive isotope. Therefore, it is possible to know when solar storms occurred in the past from the carbon 14 layer and content contained in the Antarctic ice accumulated over a long period of time. Research has shown that the Miyake Event, a solar storm with a magnitude beyond the Carrington Event, occurred around 664 C.E. Also around 993, a solar storm with a magnitude of 60% of the Miyake event occurred. Antarctic ice samples show that a Carrington event-level solar storm occurs on average about once every 500 years.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration estimates solar flare intensity on the Geomagnetic Storms scale. The geomagnetic storm scale has five levels from G1 to G5, with a larger number indicating a larger scale. Carrington events are classified as G5. Up until the Miyake event, the increase in carbon 14 was more than 10 times that of the Carrington event, so it was said to be so large that it could no longer be assessed on the geomagnetic storm scale.
In addition, when the scale exceeds the Carrington event, solar storms can generate induced currents that can destroy electrical systems on the ground. If an induced current, which can exceed 100 amps, flows into electrical components such as transformers, relays, and sensors, large-scale power outages can occur. In 1989, a solar storm three times the magnitude of the Carrington Event struck directly in Quebec, Canada. The storm damaged power grid transformers, leaving 5 million people in power outages for nine hours.
In addition, artificial satellites orbiting the earth may fail due to induced current caused by solar storms. High-frequency communication systems and submarine cables are also disrupted. Among them, GPS is heavily influenced by transportation and communication devices ranging from automobiles to airplanes to mobile phones. In addition, in the modern age, where the Internet has become an important infrastructure more than electricity, there is a risk that community activities may be completely stopped due to the influence of solar storms.
It's only a matter of time before Earth gets swept away by solar storms again, and when an Iyake event-level storm comes, it's likely to have a devastating blow worldwide, possibly taking months of power outages. It may also be important to continue research to protect power systems from the effects of solar storms.
============================
Memo 2210300119 My Thought Experiment oms Storytelling
Hubble catches rare 'echoes of light' in star explosions As a sound represents an echo, the wavelength of the expanding ego light of sample c.oss could be the fingerprint of a supernova. This suggests a set of common echo.ringe fingerprinting associations with studies reporting that the sun has radiated ring rings.
"This massive explosion of cosmic radiation from the Sun, known as the Miyake event, occurred approximately once in a thousand years, but the cause is unknown." Solar storms release many cosmic rays into Earth's upper atmosphere, producing carbon 14, a carbon radioactive isotope. Therefore, it is possible to know when the initial solar storm (oss.base) occurred in the past from the carbon 14 layer and content contained in the Antarctic ice accumulated over a long period of time. haha.
There are many stars in the universe, and magnetic storms that occur there seem to interact with oss.base.initial values of interstellar photons, echo messages of electromagnetic fields and gravitational fields. haha.
Sample a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample b.qoms(standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms(standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss(standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca
댓글