.A super-massive black hole billions of times bigger than the sun. The secret is a powerful magnetic wind
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.9
.A super-massive black hole billions of times bigger than the sun. The secret is a powerful magnetic wind
태양보다 수십억 배 초대형 블랙홀, 비밀은 강력한 자기바람
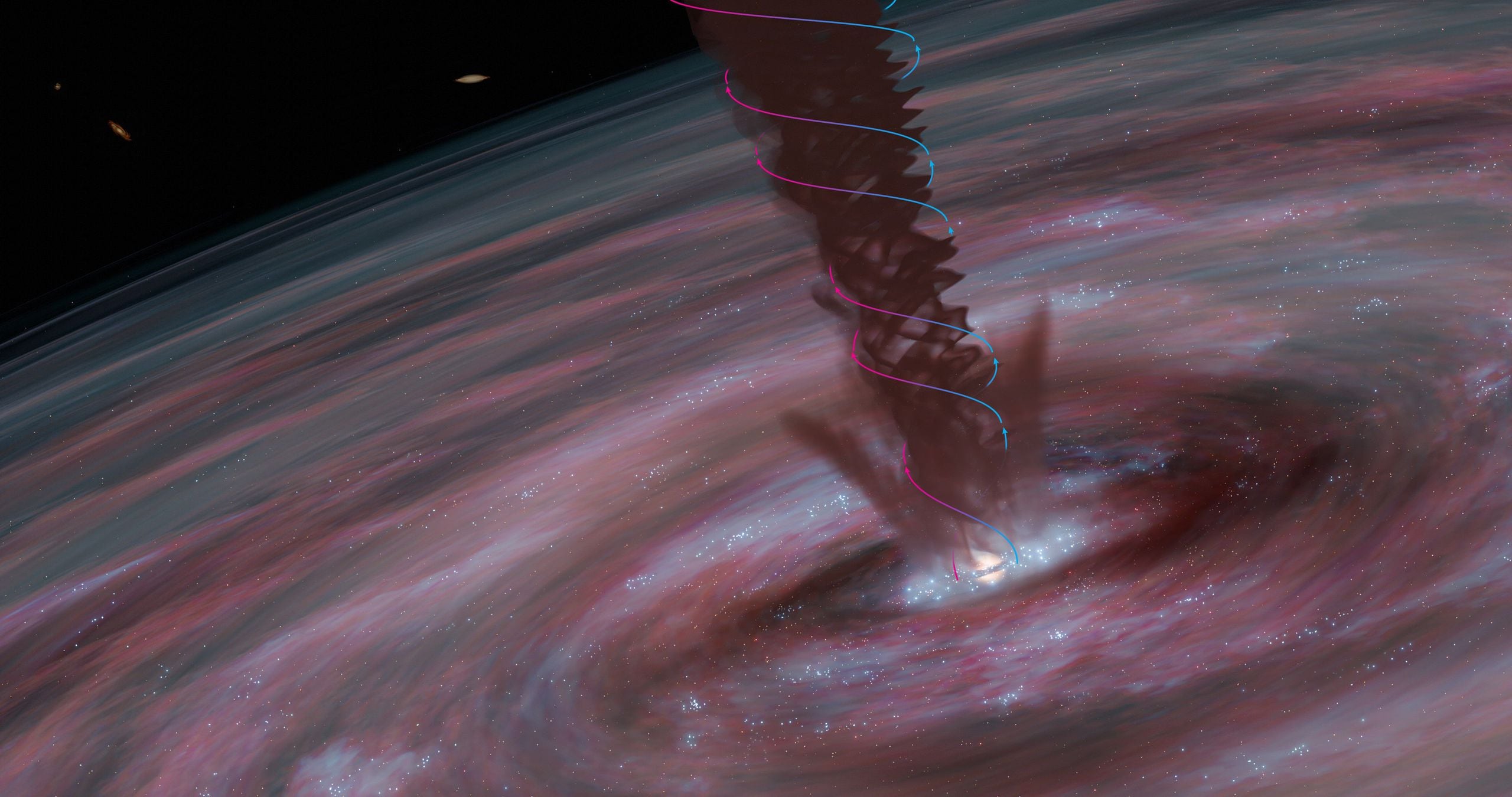
미국 노스웨스턴대·스웨덴 찰머스대 공동 연구진 블랙홀 성장, 에딩턴 한계로 제한돼 ALMA로 외부 은하 중심 블랙홀서 자기풍 존재 확인 이병철 기자(조선비즈) 입력 2024.06.21. 12:12 업데이트 2024.06.22. 15:51
미국 노스웨스턴대와 스웨덴 찰머스대 공동 연구진은 아타카마 대형 밀리미터 집합체(ALMA)로 'ESO320-G303' 은하 중심의 블랙홀에서 자기풍의 존재를 확인했다. 연구진은 자기풍이 에딩턴 한계로 제한되는 블랙홀의 성장 속도를 넘어 초대형 블랙홀로 성장할 수 있게 돕는다고 결론 내렸다./찰머스대
미국과 스웨덴의 천문학자들이 태양보다 질량이 수십억 배 큰 ‘초대형 블랙홀’이 태어나는 과정을 알아냈다. 우주에서는 초대형 블랙홀이 이미 여러 차례 발견됐다. 지금의 이론으로는 그 존재를 설명할 수 없다. 천문학계에서는 초대형 블랙홀의 존재를 ‘미스터리’로 보고 있었다. 마크 고스키 미국 노스웨스턴대 교수와 수잔 알토 스웨덴 찰스머대 교수 연구진은 21일 국제 학술지 ‘천문학과 천체물리학’에 “블랙홀 주변에서 만들어지는 강한 자기풍이 물질을 꾸준히 유입시켜 블랙홀의 성장을 돕는다는 증거를 찾았다”고 밝혔다.
블랙홀은 별이 진화 과정 마지막에서 붕괴돼 만들어지는 천체다. 별의 중심핵이 붕괴되면서 밀도가 비정상적으로 높아지면서 강한 중력을 갖는다. 처음에는 비교적 작은 크기로 시작해 시간이 지날수록 외부에서 물질을 끌어당기며 성장한다. 우주에서는 태양 질량보다 수천만~수십억 배 큰 초대형 블랙홀이 관측됐다. 그러나 천문학자들은 초대형 블랙홀이 어떻게 만들어졌는지 정확히 알지 못한다.
블랙홀 주변에서 작용하는 힘이 평형을 이루는 ‘에딩턴 한계’로 블랙홀의 성장은 느려진다. 블랙홀은 강한 중력으로 주변 물질을 빨아들이지만, 내부에서는 물질이 뿜어져 나오는 ‘제트’ 현상이 나타나기도 한다. 에딩턴 한계에 따르면 블랙홀은 100만년 동안 질량이 2%만 늘어날 수 있다. 이 정도 성장 속도로는 빅뱅이 시작된 직후 태양 질량의 100배를 넘는 블랙홀이 만들어져야만 현재 태양 질량 수십억 배 수준의 블랙홀이 만들어진다.
지금의 이론으로는 우주 곳곳에서 발견되는 초대형 블랙홀의 존재를 설명할 수가 없다. 연구진은 칠레 아타카마 사막의 해발 고도 5000m에 있는 전파망원경인 아타카마 대형 밀리미터 집합체(ALMA)로 은하 ‘ESO320-G030′을 관측했다. 이 은하는 지구가 있는 우리 은하보다 10배 빠른 속도로 별을 만드는 활동적인 은하로 알려져 있다. 은하 중심에 있는 블랙홀도 활발하게 성장하고 있다. 연구진은 적외선 파장을 관측해 은하 내부 가스인 시안화수소(HCN)의 분포를 추적했다. 그 결과, 은하 중심의 블랙홀 주변에서 이전에는 발견하지 못했던 먼지와 가스의 흐름을 포착했다.
입자가 마치 자석처럼 전하를 갖고 흐르는 ‘자기풍’이 블랙홀 주변에서 불던 것이다. 알토 교수는 “초대형 블랙홀이 만들어지려면 제트방출과 중력 외에 또다른 힘이 존재해야 한다”며 “자기풍이 블랙홀의 성장을 가속하는 요인으로 보인다”고 말했다. 연구진은 자기풍에 따른 블랙홀의 성장 과정을 배수구에 비유했다. 물이 배수구 주변에서 회오리를 일으키면서 더 빠르게 빨려들어가듯 블랙홀에서도 자기풍으로 물질이 더 쉽게 흘러간다는 것이다.
고스키 교수는 “별이 성장할 때도 초기에는 자기풍이 결정적인 역할을 하는 것으로 알려져 있다”며 “초대형 블랙홀에서도 비슷하지만 훨씬 더 거대한 현상이 성장을 촉진할 것”이라고 말했다. 연구진은 이번 연구 결과를 다른 은하로 확장해 초대형 블랙홀 형성의 비밀을 풀어낸다는 계획이다. 자기풍이 ESO320-G030 은하 이외에서도 흔하게 나타나는 현상이라면 그간 미스터리로 남아 있던 초대형 블랙홀의 존재를 설명할 수 있을 전망이다. 고스키 교수는 “자기풍이 블랙홀 내부로의 물질 유입을 가속하는 과정에 대해서는 추가적인 연구가 필요하다”며 “다만 초대형 블랙홀 형성에 결정적인 역할을 한다는 점은 명확하다”고 말했다.
참고 자료 Astronomy and Astrophysics(2024), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202348821
메모 2406230515
나의 oms.vix.ain이론은 블랙홀의 자기풍 원인에 관한 데이타를 지지한다. 자기풍은 xy 전자기풍으로 편향적 스핀풍 키랄대칭성 회전 탓이다. 그 샘플이 바로 보기1.이다. 세로의 중심축으로 부터 반을 접으면 회전도어의 궤도가 나타난다. 그 샘플이 무지막지하게 크고 조밀하게 겹치면 블랙홀을 시뮬레이션된다. 중요한 사실은 이 보기1.이 하나의 원리에서 시작된 점이다. oms.vix.ain이라는 거대한 원같은 다각형의 vix.vixxer.spin.bar citadel 때문이다. 이것을 본인이 직접 작년에 찾아냈다. 허허.
보기1.
vix.a'6//vixx.a(b1,g3,k3,o5,n6)
b0acfd|0000e0
000ac0|f00bde
0c0fab|000e0d
e00d0c|0b0fa0
f000e0|b0dac0
d0f000|cae0b0
0b000f|0ead0c
0deb00|ac000f
ced0ba|00f000
a0b00e|0dc0f0
0ace00|df000b
0f00d0|e0bc0a
문제는 하수구 처럼 빨리듯 돌아가는 현상을 vixer의 급속한 성장으로 해석하는데 msoss을 적용하는 게 지금은 막 생각났기 때문이다. 허허.
소스1.
블랙홀은 별이 진화 과정 마지막에서 붕괴돼 만들어지는 천체다. 별의 중심핵이 붕괴되면서 밀도가 비정상적으로 높아지면서 강한 중력을 갖는다. 처음에는 비교적 작은 크기로 시작해 시간이 지날수록 외부에서 물질을 끌어당기며 성장한다.
우주에서는 태양 질량보다 수천만~수십억 배 큰 초대형 블랙홀이 관측됐다. 그러나 천문학자들은 초대형 블랙홀이 어떻게 만들어졌는지 정확히 알지 못한다. 블랙홀 주변에서 작용하는 힘이 평형을 이루는 ‘에딩턴 한계’로 블랙홀의 성장은 느려진다. 블랙홀은 강한 중력으로 주변 물질을 빨아들이지만, 내부에서는 물질이 뿜어져 나오는 ‘제트’ 현상이 나타나기도 한다.
에딩턴 한계에 따르면 블랙홀은 100만년 동안 질량이 2%만 늘어날 수 있다. 이 정도 성장 속도로는 빅뱅이 시작된 직후 태양 질량의 100배를 넘는 블랙홀이 만들어져야만 현재 태양 질량 수십억 배 수준의 블랙홀이 만들어진다. 지금의 이론으로는 우주 곳곳에서 발견되는 초대형 블랙홀의 존재를 설명할 수가 없다.
연구진은 적외선 파장을 관측해 은하 내부 가스인 시안화수소(HCN)의 분포를 추적했다. 그 결과, 은하 중심의 블랙홀 주변에서 이전에는 발견하지 못했던 먼지와 가스의 흐름을 포착했다. 입자가 마치 자석처럼 전하를 갖고 흐르는 ‘자기풍’이 블랙홀 주변에서 불던 것이다.
알토 교수는 “초대형 블랙홀이 만들어지려면 제트방출과 중력 외에 또다른 힘이 존재해야 한다”며 “자기풍이 블랙홀의 성장을 가속하는 요인으로 보인다”고 말했다.
연구진은 자기풍에 따른 블랙홀의 성장 과정을 배수구에 비유했다. 물이 배수구 주변에서 회오리를 일으키면서 더 빠르게 빨려들어가듯 블랙홀에서도 자기풍으로 물질이 더 쉽게 흘러간다는 것이다.
고스키 교수는 “별이 성장할 때도 초기에는 자기풍이 결정적인 역할을 하는 것으로 알려져 있다”며 “초대형 블랙홀에서도 비슷하지만 훨씬 더 거대한 현상이 성장을 촉진할 것”이라고 말했다.
1.
보기1. oms.vix.ain이 자기장 스핀파가 작동하는 블랙홀이 맞다면 msbase.oss을 따라가며 커지는 우주의 시공간을 닮은 것이다. 문제는 역삼각형이 banc탓이면 일정한 크기로 자란 별의 주검과 맞아 떨어진다. 역성장 시나리오이다. 허허.

Memo 2406230515
My oms.vix.ain theory is supported by data regarding the cause of the black hole's magnetic wind. The magnetic wind is an xy electromagnetic wind, which is due to the rotation of the chiral symmetry of the biased spin wind. The sample is example 1. When folded in half from the vertical central axis, the orbit of the rotating door appears. If the samples are extremely large and densely overlapped, a black hole is simulated. The important fact is that Example 1 started from one principle. This is because of the vix.vixxer.spin.bar citadel of a huge circle-like polygon called oms.vix.ain. I found this myself last year. haha.
Example 1.
vix.a'6//vixx.a(b1,g3,k3,o5,n6)
b0acfd|0000e0
000ac0|f00bde
0c0fab|000e0d
e00d0c|0b0fa0
f000e0|b0dac0
d0f000|cae0b0
0b000f|0ead0c
0deb00|ac000f
ced0ba|00f000
a0b00e|0dc0f0
0ace00|df000b
0f00d0|e0bc0a
The problem is that I just remembered how to apply msoss to interpret the phenomenon of running fast like a sewer as the rapid growth of vixers. haha.
Source 1.
A black hole is a celestial body created when a star collapses at the end of its evolution process. As the star's core collapses, its density increases abnormally, creating a strong gravitational force. It starts out relatively small in size and grows over time by attracting materials from the outside.
Supermassive black holes tens of millions to billions of times larger than the mass of the sun have been observed in space. However, astronomers do not know exactly how supermassive black holes were created. The growth of the black hole slows down due to the ‘Eddington limit’, where the forces acting around the black hole become balanced. Black holes suck in surrounding matter with strong gravity, but a ‘jet’ phenomenon in which matter is ejected from the inside also appears.
According to the Eddington limit, a black hole can only gain 2% of its mass in one million years. At this growth rate, a black hole with a mass exceeding 100 times that of the sun would have to be created immediately after the Big Bang began to create a black hole that is currently billions of times the mass of the sun. Current theories cannot explain the existence of supermassive black holes found throughout the universe.
The researchers tracked the distribution of hydrogen cyanide (HCN), a gas inside the galaxy, by observing infrared wavelengths. As a result, they captured previously undiscovered flows of dust and gas around the black hole at the center of the galaxy. A ‘magnetic wind’, in which particles flow with electric charge like a magnet, blew around the black hole.
Professor Aalto said, “For a supermassive black hole to be created, another force must exist in addition to jet emission and gravity,” and added, “Magnetic wind appears to be a factor that accelerates the growth of black holes.”
The researchers compared the growth process of a black hole due to magnetic wind to a drain. Just as water is sucked in faster as it creates a whirlwind around a drain, matter flows more easily through a black hole due to magnetic winds.
Professor Gorsky said, “It is known that magnetic winds play a decisive role in the early stages of star growth,” and added, “For supermassive black holes, a similar but much more massive phenomenon will promote growth.”
One.
Example 1. If oms.vix.ain is a black hole in which magnetic spin waves operate, it resembles the space-time of the universe growing along with msbase.oss. The problem is that if the inverted triangle is banc, it matches the corpse of a star that has grown to a certain size. It is a reverse growth scenario. haha.
댓글