.Unlocking Quantum Superconductivity Mysteries With Ultracold Fermions
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.54
.Unlocking Quantum Superconductivity Mysteries With Ultracold Fermions
초저온 페르미온으로 양자 초전도의 미스터리 풀기

주제:중국과학원페르미온스입자물리학초전도성 2024년 2월 7일 중국 과학원 페르미온 쌍 입자 물리학 컨셉 아트 연구자들은 거의 20년 동안 논쟁의 주제였던 단위 페르미 가스의 다체 쌍 유사 간격을 관찰하고 정량적으로 특성화함으로써 양자 물리학에서 획기적인 발견을 했습니다. 이번 발견은 이러한 가스의 유사갭의 특성에 대한 오랜 의문을 해결할 뿐만 아니라 고온 초전도체에서 관찰되는 유사갭과의 잠재적 연관성을 제시합니다. 신용: SciTechDaily.com
연구자들은 단일 페르미 가스에서 다체 쌍을 이루는 유사 간격을 결정적으로 관찰하여 초전도 메커니즘에 대한 이해를 향상시켰습니다. 중국과학원 산하 중국과기대(USTC)의 Jianwei Pan, Xingcan Yao, Yu'ao Chen 교수가 이끄는 연구팀이 처음으로 다체 쌍을 관찰하고 정량적으로 특성화했습니다. 단일 페르미 기체의 의사갭. 극저온 원자 공동체가 거의 20년 동안 추구해 온 이 성과는 이들 가스에 쌍을 이루는 유사 간격이 존재하는지에 관한 오랜 논쟁을 해결했습니다. 또한 미리 형성된 쌍 초전도 이론의 틀 내에서 고온 초전도체의 의사갭의 가능한 원인으로 쌍을 지원합니다.
2월 7일 Nature 에 게재된 이 연구는 다가오는 용의 해와 일치합니다. 흥미롭게도, 이 성취 뒤에 숨은 물리학은 중국 문화의 큰 성공을 상징하는 "용문 위로 뛰어오르는 잉어"라는 상징적인 중국 신화에서 생생하게 설명될 수 있습니다. 용문 페르미온스를 뛰어넘는 잉어 이 예술적 표현에서 입에 옥구슬을 물고 있는 두 마리의 잉어는 반대 방향으로 회전하는 페르미온을 상징합니다.
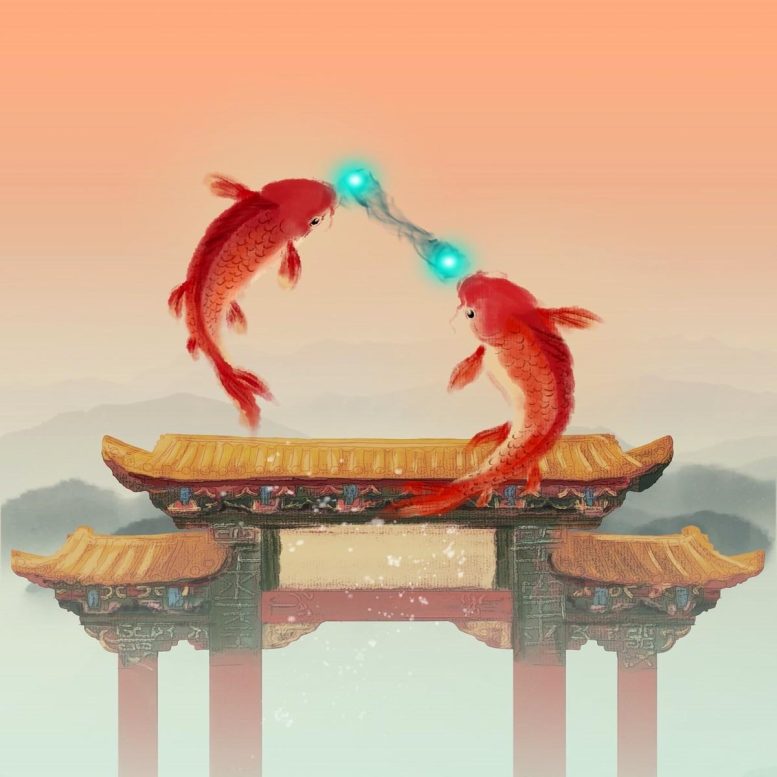

드래곤 게이트(Dragon Gate)는 초유체 전이와 의사갭을 모두 나타냅니다. 용문 위로 뛰어오르는 잉어의 묘사는 초유체 상전이 온도 이상의 쌍을 암시합니다. 이러한 페어링 현상은 결국 의사갭(pseudogap)의 출현으로 이어집니다. 크레딧: Lei Chen
초전도성의 신비를 풀다 에너지 갭의 존재는 초전도성의 특징적인 현상입니다. 기존의 초전도체에서는 초전도 전이온도(T c ) 아래에서 에너지 갭이 존재합니다. 놀랍게도, 큐레이트 고온 초전도체에서는 Tc 이상에서도 에너지 갭이 여전히 관찰될 수 있는데 , 이는 유사 갭(pseudogap)으로 알려진 현상입니다. 의사갭의 기원과 특성을 이해하는 것은 특히 쿠퍼 쌍이 장거리 위상 일관성을 형성하고 설정하는 방법과 관련하여 고온 초전도 메커니즘을 파악하는 데 중요합니다. pseudogap의 기원에 대한 두 가지 주요 가설이 있습니다. 이는 강한 쌍 변동으로 인해 발생하며, Tc 이상에서 미리 형성된 전자 쌍으로 나타나고 응집성 쌍 응축의 전조 역할을 합니다. 이는 반강자성 순서, 스트라이프 위상 및 쌍 밀도 파동과 같은 고온 초전도체의 다양한 양자 순서에서 발생합니다. 그러나 고온 초전도 물질의 복잡성으로 인해 이러한 질문에 대한 답은 거의 나오지 않습니다.
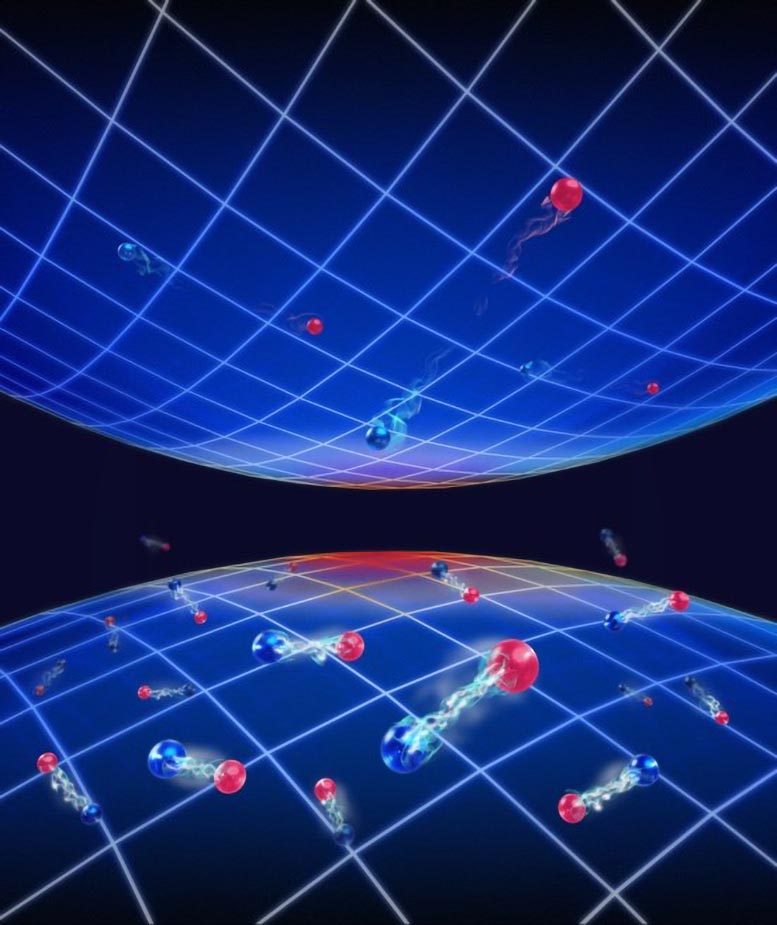
임계 온도 이상에서 측정된 단일 입자 스펙트럼 기능 빨간색과 파란색 구체는 각각 위쪽 및 아래쪽 스핀을 갖는 페르미온 원자를 상징합니다. 그리드가 있는 곡면은 준입자의 운동량-에너지 지형을 나타냅니다. 짝을 이루는 페르미온은 아래쪽 표면에 서식하고 짝을 이루지 않은 페르미온은 위쪽 표면을 차지합니다. 표면 사이의 간격은 유사 간격을 나타내며, 이는 페르미온 쌍을 깨는 데 최소한의 에너지가 필요함을 나타냅니다. 간격에 흐릿한 페르미온 쌍은 유사 간격이 부분적으로 채워져 있음을 나타냅니다. 크레딧: Lei Chen
양자 시뮬레이션이 새로운 빛을 밝힙니다 단일 페르미 가스는 쌍을 이루는 의사갭의 존재와 특성을 조사하기 위한 이상적인 양자 시뮬레이션 플랫폼을 제공합니다. 이는 전례 없는 제어 가능성, 순도, 그리고 가장 중요하게는 알려진 단거리 매력적인 상호 작용의 존재 때문일 수 있습니다. 또한 벌크 페르미 가스에 격자 구조가 없기 때문에 경쟁하는 양자 순서의 영향이 제거됩니다.
이러한 맥락에서 이전 실험에서는 강하게 상호 작용하는 페르미 가스의 트랩 평균 단일 입자 스펙트럼 기능을 측정했습니다. 그러나 이러한 실험은 주로 트랩의 불균일성과 일반적으로 사용되는 rf 분광학의 최종 상태 상호 작용으로 인해 발생하는 심각한 문제로 인해 의사 간격에 대한 설득력 있는 증거를 제공하지 못했습니다. USTC 연구팀은 수년간의 헌신적인 연구 끝에 초저온 리튬과 디스프로슘 원자를 활용한 양자 시뮬레이션 플랫폼을 구축하고, 균일한 페르미 가스의 최첨단 준비를 달성했습니다( Science ). 또한 이 팀은 필요한 자기장을 안정화하기 위한 새로운 기술을 개발했습니다.
약 700G의 자기장에서 달성된 단기 변동은 25μG 미만으로 기록적으로 높은 상대 자기장 안정성을 제공합니다. 이러한 극도로 안정적인 자기장을 통해 연구팀은 마이크로파 펄스를 사용하여 원자를 초기 상태와 상호 작용하지 않는 높은 에너지 상태로 여기시켜 운동량 분해 광전자 방출 분광학을 실현할 수 있었습니다. 이 두 가지 중요한 기술 혁신을 통해 연구팀은 서로 다른 온도에서 단일 페르미 가스의 단일 입자 스펙트럼 기능을 체계적으로 측정하고 짝짓기 의사갭의 존재를 관찰하여 초유체의 전조로서 미리 형성된 짝짓기의 역할을 뒷받침했습니다.
, 연구팀은 강하게 상호작용하는 양자계의 거동을 특성화하는 데 필수적인 양인 측정된 스펙트럼 함수로부터 페어링 갭, 쌍 수명 및 단일 입자 산란 속도를 결정했습니다. 이러한 발견은 강하게 상관된 시스템에 대한 연구를 발전시킬 뿐만 아니라 적절한 다체 이론을 확립하는 데 귀중한 통찰력과 정보를 제공합니다. 이 연구에서 개발된 기술은 단일 밴드 초유체성, 스트라이프 위상 및 Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov 초유체성과 같은 다른 중요한 저온 양자 위상에 대한 향후 탐사 및 연구를 위한 기반을 마련합니다.
참조: 2024년 2월 7일, Nature . DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06964-y
https://scitechdaily.com/unlocking-quantum-superconductivity-mysteries-with-ultracold-fermions/
메모 240208_0321,0453 나의 사고실험 qpeoms 스토리텔링
고온 초전도체 현상을 나타내는 현상에는 의사갭이 존재하는데 이것은 마치 구분되어지는 페르미온 단일 쌍1+1과 짝을 이루지 않는 다중 1,1의 분포에 틈이 존재하는 것 처럼 보인다.
이는 quxe들과 lenser가 서로 다른 표면을 가지 틈이 존재하늗 것처럼 보이게 한다.
qms이론에서의 유사간격은 에너지와 물질의 경계처럼 보이는데 이는 에너지가 쌍을 이루지 않는 상태의 무질서한 1,1의 전자 분포의 기체상태를 나타냄과는 달리 1+1의 질량을 고체이다. 달리 표현하면 가체와 고체층 사이에 pseudogap이 있는 형국이다.
이는 우주에서 성운의 가스층으로 부터 별들이 생겨나는 원리와 유사하다. primordial_disk.gas.quaser(표현어 유래: qvix,qix,qux,)들이 별을 형성하는 핵융합체 lenser 표면층과의 사이에 '1:multiple의 틈이 존재할 수 있다'는 뜻이다.
달리 생각하여 보면, 많은 가스 내부에 작은 빛이 생겨나는 모습이 공간적인 틈이 존재하는 것이 바, 특히 고온초도체에 대해서도 '일반적인 양자현상'이 나타날 수도 있다는 것이다. 허허.

Source 1.
Unraveling the mystery of superconductivity
The existence of an energy gap is a characteristic phenomenon of superconductivity. In conventional superconductors, an energy gap exists below the superconducting transition temperature (T c ). Surprisingly, in curated high-temperature superconductors, an energy gap can still be observed above Tc, a phenomenon known as pseudogap.
Understanding the origin and nature of the pseudogap is important for understanding the mechanisms of high-temperature superconductivity, especially with regard to how Cooper pairs form and establish long-range phase coherence.
There are two main hypotheses about the origin of the pseudogap. This arises due to strong pair fluctuations, which appear as preformed electron pairs above Tc and serve as a precursor to coherent pair condensation. This occurs in various quantum orders in high-temperature superconductors, such as antiferromagnetic order, stripe phase, and pair density wave. However, the complexity of high-temperature superconducting materials leaves these questions rarely answered.
The red and blue spheres symbolize fermion atoms with up and down spins, respectively. The gridded surface represents the momentum-energy landscape of the quasiparticle. Paired fermions populate the lower surface, while unpaired fermions occupy the upper surface. The spacing between the surfaces exhibits pseudospacing, indicating that minimal energy is required to break a fermion pair. A pair of fuzzy fermions in the gap indicates that the pseudogap is partially filled.
Note 1. Similar gap
When a phase transition occurs between a superconductor and an ordinary solid (insulator or conductor), the electrical conductivity becomes infinite and the energy distribution of electrons changes. In a general conductor, the energy levels of electrons are distributed continuously around the Fermi energy level, so electrons have continuous energy values around the Fermi energy. However, in a superconductor, the areas where electrons can exist slightly above and slightly below the Fermi energy level are limited, so there is a band gap in the allowed energy levels (values) of electrons. This can be obtained by observing the differential value of electrical conductivity of a superconductor sample using a scanning tunneling microscope. And in the case of high-temperature superconductors, holes in this energy level exist even in the temperature range where superconductivity does not occur, so they are called pseudogaps.
pseudogap
In condensed matter physics, a pseudogap refers to a state in which the Fermi surface of a material has a partial energy gap. For example, it refers to a band structure state in which the Fermi surface has gaps only at certain points.
State diagram of a doped cuprate superconductor showing pseudogap steps.
The term 'pseudogap' was coined by Nevill Mott in 1968, which refers to the Coulomb repulsion between electrons in the same atom, the band gap in disordered materials, or a combination of these.
In a modern context, pseudogap is a term in the field of high-temperature superconductivity that refers to an energy range (usually near the Fermi level) in which there are few associated states. This is very similar to a real 'interval', which is a range of energies that do not contain any allowed states. These gaps open, for example, when electrons interact with the lattice. The pseudogap phenomenon is observed in the region of the general phase diagram curating the high-temperature superconductors present in the underdoped specimen at temperatures above the superconducting transition temperature.
Only certain electrons ‘see’ this gap. The gap that must be associated with an insulating state exists only for electrons moving parallel to the copper-oxygen bond. [3] Electrons moving at 45° to this bond are free to move throughout the crystal. Therefore, the Fermi surface consists of Fermi arcs that form a pocket at the center of the edge of the Brillouin zone. In the pseudogap phase, these arcs gradually disappear as the temperature decreases until only four points on the diagonal of the Brillouin zone remain gapless.
On the one hand, this could represent a completely new electronic phase that consumes the available states, leaving only a few states capable of pairing and superconducting. On the other hand, the similarity between this partial gap and the gap in the superconducting state may indicate that the pseudogap originates from preformed Cooper pairs.
Recently, pseudogap states have also been reported in highly disordered conventional superconductors such as TiN, NbN, or granular aluminum.
The existence of pseudogaps is strong experimental evidence for the absence of Cooper pairs. The pseudo-gap acts as a superconducting gap below the critical temperature. For this reason, although there is a pseudo-gap in low-temperature superconductors, the gap is so small that it appears not to be observed due to thermal fluctuations.
=================================================
Memo 240208_0321,0453 My thought experiment qpeoms storytelling
There is a pseudo-gap in the phenomenon that represents the high-temperature superconductor phenomenon, which looks as if there is a gap in the distribution of the single 1+1 pair of distinct fermions and the unpaired multiple 1,1.
This makes it appear as if there are gaps between the quxes and the lenser on different surfaces.
The pseudo-interval in qms theory looks like the boundary between energy and matter. Unlike the gaseous state of disordered 1,1 electron distribution in which energy is not paired, it is a solid with a mass of 1+1. In other words, there is a pseudogap between the gaseous body and the solid layer.
This is similar to the principle by which stars are formed from the gas layer of a nebula in space. It means that 'a gap of 1:multiple may exist' between the primordial_disk.gas.quaser (expression origin: qvix, qix, qux,) and the surface layer of the nuclear fusion lenser that forms stars.
If you think about it another way, the appearance of small light inside many gases indicates the existence of a spatial gap, so a 'general quantum phenomenon' may also appear, especially for high-temperature superconductors. haha.
Sample oms.vix.a (standard2)
2401030806
vix.a'6//vixx.a(b1,g3,k3,o5,n6)
b0acfd0000e0
000ac0f00bde
0c0fab000e0d
e00d0c0b0fa0
f000e0b0dac0
d0f000cae0b0
0b000f0ead0c
0deb00ac000f
ced0ba00f000
a0b00e0dc0f0
0ace00df000b
0f00d0e0bc0a
sample qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample pms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
Sample oss.msbase (standard) -7.5%
zxdxybzyz- zxxyzyz00
zxdzxezxz- zxzxzxz00
xxbyyxzzx- xxyyxzzx0
zybzzfxzy- zyzzxzy00
cadccbcdc-000000000
cdbdcbdbb- 000000000
xzezxdyyx- xzzxyyx00
zxezybzyy- zxzyzyy00
bddbcbdca-000000000

.A long, long time ago in a galaxy not so far away: Research unearths clues to conditions of the early universe
아주 오래전, 그리 멀지 않은 은하계에서: 연구를 통해 초기 우주 상태에 대한 단서 발견
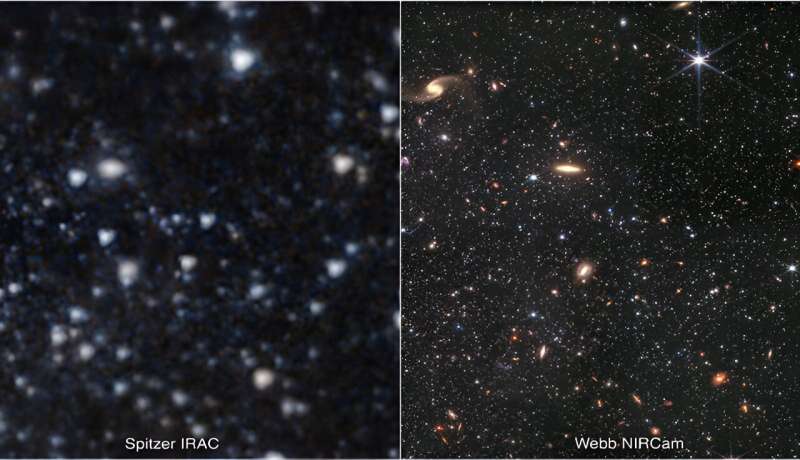

러트 거스 대학교 WLM 은하의 일부에 대한 두 가지 모습. 하나는 NASA의 허블 우주 망원경(왼쪽)으로 촬영한 것이고, 두 번째는 제임스 웹 우주 망원경으로 촬영한 것입니다. 출처: NASA/ESA/CSA/IPAC/Kristen McQuinn-Rutgers University Rutgers University-New Brunswick FEBRUARY 6, 2024
천문학자가 이끄는 연구팀은 NASA의 James Webb 우주 망원경을 통해 수집된 대규모 데이터 세트를 사용하여 초기 우주에 존재하는 조건에 대한 단서를 발굴하고 있습니다. 연구진에 따르면 연구팀은 WLM(Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte) 은하에 있는 별들의 나이를 분류하여 지금까지 가장 상세한 그림을 구축했다고 합니다. 은하수의 이웃인 WLM은 130억년 전에 형성된 고대 별을 포함하는 별 형성의 활발한 중심지입니다.
"매우 깊이 관찰하고 명확하게 관찰함으로써 우리는 효과적으로 시간을 되돌릴 수 있었습니다."라고 인문과학대학 물리학 및 천문학과 조교수인 크리스틴 맥퀸(Kristen McQuinn)은 말했습니다. The Asphysical Journal 에 설명된 연구 입니다 . "당신은 기본적으로 우주 역사 초기에 형성된 매우 낮은 질량의 별을 찾기 위해 일종의 고고학 발굴을 진행하고 있습니다."
McQuinn은 Rutgers Office of Advanced Research Computing에서 관리하는 Amarel 고성능 컴퓨팅 클러스터를 통해 팀이 은하계의 항성 개발 역사를 계산할 수 있게 되었다고 평가했습니다. 연구의 한 측면에는 하나의 대규모 계산을 수행하고 이를 600번 반복하는 것이 포함되었다고 McQuinn은 말했습니다. 주요 계산 노력은 또한 더 넓은 과학계에 도움이 될 망원경 교정 및 데이터 처리 절차를 확인하는 데 도움이 되었다고 그녀는 덧붙였습니다.
-소위 "낮은 질량" 은하들은 McQuinn의 특별한 관심 대상입니다. 그들은 초기 우주를 지배했다고 믿기 때문에 연구자들은 별의 형성, 화학 원소의 진화, 별 형성이 은하의 가스와 구조에 미치는 영향을 연구할 수 있습니다. 희미하고 하늘을 가로질러 퍼져 있는 그들은 지역 우주에 있는 은하의 대부분을 구성합니다. Webb과 같은 고급 망원경을 사용하면 과학자들이 더 자세히 볼 수 있습니다.
WLM(나선형이나 타원형 등 뚜렷한 모양을 갖고 있지 않다는 뜻의 "불규칙" 은하)은 1909년 독일 천문학자 맥스 볼프(Max Wolf)에 의해 발견되었으며 1926년 스웨덴 천문학자 크누트 룬드마크(Knut Lundmark)와 영국 천문학자에 의해 더 자세히 특성화되었습니다. 필리베르 자크 멜로트. 이 은하는 은하수를 포함하는 아령 모양의 은하군인 국부은하군 외곽에 위치합니다. 국부은하군의 가장자리에 있기 때문에 WLM은 다른 은하계 와의 혼합으로 인한 피해로부터 보호 되어 WLM의 별 인구는 깨끗한 상태로 연구에 유용하다고 McQuinn은 지적했습니다.
WLM은 또한 많은 양의 가스가 포함되어 활발하게 별을 형성할 수 있는 역동적이고 복잡한 시스템이기 때문에 천문학자들에게 흥미로운 곳입니다. 은하의 별 형성 역사(우주의 다양한 시대에 걸쳐 별이 탄생하는 속도)를 공식화하기 위해 McQuinn과 그녀의 팀은 망원경을 사용하여 수십만 개의 개별 별이 포함된 하늘의 범위를 공들여 영점으로 조정했습니다. 별의 나이를 결정하기 위해 그들은 온도의 대리자인 별의 색상과 밝기를 측정했습니다.
-McQuinn은 "우리는 별의 진화에 대해 우리가 알고 있는 정보와 이러한 색상과 밝기가 나타내는 것을 기본적으로 은하의 별의 나이에 따라 사용할 수 있습니다"라고 말했습니다. 그런 다음 연구원들은 다양한 연령의 별을 세고 역사에 걸쳐 별의 탄생률을 계획했다고 덧붙였습니다. 우주. "결국 당신이 보고 있는 이 구조가 얼마나 오래되었는지에 대한 감각이 생깁니다."
-이러한 방식으로 별을 분류하는 것은 연구원들에게 WLM의 별 생성 능력이 시간이 지남에 따라 썰물과 흐름을 반복한다는 것을 보여주었습니다. 허블 우주 망원경을 사용하는 과학자들의 이전 평가를 확인한 팀의 관찰은 은하계가 우주 역사 초기에 30억 년에 걸쳐 별을 생성했음을 보여줍니다. 잠시 멈췄다가 다시 활성화되었습니다. McQuinn은 정지가 초기 우주의 특정 조건에 의해 발생했다고 믿고 있다고 말했습니다. “그때 우주는 정말 뜨거웠어요.” 그녀가 말했다.
-"우리는 우주의 온도가 결국 이 은하계의 가스를 가열하게 되었고 잠시 동안 별 형성이 꺼졌다고 생각합니다. 냉각 기간은 수십억 년 동안 지속된 후 별 형성이 다시 진행되었습니다."
이 연구는 지정된 과학자들이 우주망원경과학연구소(Space Telescope Science Institute)와 협력하여 Webb의 능력을 강조하고 천문학자들이 미래 관측을 준비할 수 있도록 돕기 위해 고안된 연구를 수행하는 NASA의 조기 출시 프로그램(Early Release Program)의 일부입니다.
NASA는 2021년 12월 Webb 망원경을 출시했습니다. 대형 거울 기구는 지구에서 백만 마일 떨어진 태양 주위를 공전합니다. 과학자들은 초기 우주의 조건, 태양계의 역사, 외계 행성 탐색 등 다양한 주제를 연구하기 위해 망원경에서 시간을 두고 경쟁합니다. McQuinn은 "아직 완료되지 않은 이 프로그램에서 나올 많은 과학이 있습니다"라고 말했습니다. 이 연구에 참여한 다른 Rutgers 연구자로는 Rutgers School of Arts and Sciences의 물리학 및 천문학과에서 박사 과정을 밟고 있는 Max Newman과 박사후 연구원인 Roger Cohen이 있습니다.
추가 정보: 크리스틴. BW McQuinn 외, JWST 해결된 항성 개체군 조기 출시 과학 프로그램. IV. 국부은하군 WLM의 별 형성 역사, 천체물리학 저널 (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad1105 저널 정보: 천체 물리학 저널 러트거스대학교 제공
https://phys.org/news/2024-02-galaxy-unearths-clues-conditions-early.html
==================================
메모 2402080533 나의 사고실험 qpeoms 스토리텔링
msbase는 전형적인 우주적인 별들이 모여서 생긴 구조의 완성체인 마방진이다. 그런데 유사 마방진이 엄청나게 존재한다. 이를 qms_base로 표현되어질 수 있다. 하나는 ms_base가 되어가는 미성숙된 과정의 미완성에서의 질량이 낮은 초기 우주를 연상 시킬 수 있다. 허허.
이는 우주의 별 생성 능력이 시간이 지남에 따라 썰물과 흐름을 반복한다는 것을 보여준다. 허허. 물론 완성체 우주는 ms_base.oss로 인하여 폭발적 발화점 연쇄반응의 진화를 거듭한다. 우리 우주가 거대한 다중우주의 입자크기의 일원임을 알게 한다. 허허.

“We can use what we know about the evolution of stars and what these colors and brightnesses represent, basically based on the ages of the stars in the galaxy,” McQuinn said. The researchers then counted stars of different ages and plotted their birth rates throughout history, he added. universe. “Ultimately you get a sense of how old this structure you’re looking at is.”
- Classifying stars in this way showed researchers that the WLM's star-forming ability ebbs and flows over time. The team's observations, confirming previous assessments by scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope, show that galaxies formed stars over a period of 3 billion years early in the history of the universe. It paused for a moment and then became active again. McQuinn said he believes the halt was caused by specific conditions in the early universe. “Space was really hot back then.” She said.
-"We think that the temperature of the universe eventually heated up the gas in these galaxies and star formation turned off for a while. The cooling period lasted billions of years, and then star formation got underway again."
-So-called “low-mass” galaxies are of special interest to McQuinn. Because they are believed to have dominated the early universe, researchers can study star formation, the evolution of chemical elements, and how star formation affects the gas and structure of galaxies. Faint and spread across the sky, they make up most of the galaxies in our local universe. Advanced telescopes like the Webb allow scientists to see even more detail.
=================================================
Memo 2402080533 My thought experiment qpeoms storytelling
msbase is a magic square, a completed structure created by typical cosmic stars gathered together. However, there are a ton of pseudo-magic squares. This can be expressed as qms_base. One can be reminiscent of the low-mass early universe in the immature process of becoming ms_base. haha.
This shows that the universe's star-forming capacity ebbs and flows over time. haha. Of course, the complete universe continues to evolve in an explosive ignition chain reaction due to ms_base.oss. It makes us realize that our universe is a particle-sized member of a huge multiverse. haha.
Sample oms.vix.a (standard2)
2401030806
vix.a'6//vixx.a(b1,g3,k3,o5,n6)
b0acfd0000e0
000ac0f00bde
0c0fab000e0d
e00d0c0b0fa0
f000e0b0dac0
d0f000cae0b0
0b000f0ead0c
0deb00ac000f
ced0ba00f000
a0b00e0dc0f0
0ace00df000b
0f00d0e0bc0a
sample qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample pms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
Sample oss.msbase (standard) -7.5%
zxdxybzyz- zxxyzyz00
zxdzxezxz- zxzxzxz00
xxbyyxzzx- xxyyxzzx0
zybzzfxzy- zyzzxzy00
cadccbcdc-000000000
cdbdcbdbb- 000000000
xzezxdyyx- xzzxyyx00
zxezybzyy- zxzyzyy00
bddbcbdca-000000000
댓글