.Cooling 100 million degree plasma with a hydrogen-neon mixture ice pellet
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
http://jk0620.tripod.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.9
.Cooling 100 million degree plasma with a hydrogen-neon mixture ice pellet
수소-네온 혼합 얼음 알갱이로 1억도 플라즈마 냉각
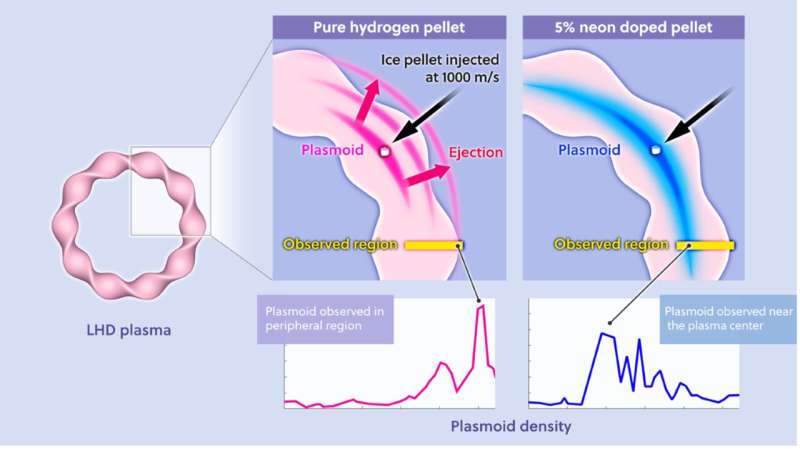
국립 자연과학 연구소 순수 수소와 5% 네온이 혼합된 수소의 플라스모이드 거동. 이 실험에서는 (전례 없는 속도인) 20kHz에서 작동하는 새로운 Thomson Scattering(TS) 진단 시스템을 사용하여 (i) 플라스모이드가 관찰 영역을 통과하는 순간의 밀도를 측정하고 (ii) 다음을 식별했습니다. 이론적 예측을 확인한 위치. 출처: 국립융합과학연구소 JANUARY 6, 2023
현재 국제 협력을 통해 프랑스에서 건설 중인 세계 최대의 실험용 핵융합로인 ITER에서 소위 "교란"을 통한 고온 플라즈마의 자기 구속의 갑작스러운 종료는 주요 공개 문제를 제기합니다. 이에 대한 대책으로 플라즈마 불안정 징후가 감지되면 플라즈마를 강제로 냉각시키는 중단 완화 기술이 전 세계적으로 집중 연구 대상이다.
-이제 국립 양자 과학 기술 연구소(QST)와 국립 과학 연구소(NINS)의 국립 융합 과학 연구소(NIFS)의 일본 연구원 팀은 수소 얼음 알갱이에 약 5%의 네온을 첨가함으로써 순수한 수소 얼음 알갱이가 주입될 때보다 표면 아래에서 플라즈마를 더 깊게 냉각할 수 있으므로 더 효과적으로 냉각할 수 있습니다.
연구원들은 NIFS 소유의 Large Helical Device에서 이론 모델 과 고급 진단을 통한 실험적 측정을 사용 하여 얼음 펠릿 주변에 형성되는 고밀도 플라스모이드의 역학을 규명하고 강제 냉각 시스템의 성공적인 성능 향상을 담당하는 물리적 메커니즘을 식별했습니다.
ITER에서 실험을 수행하는 데 없어서는 안될 필수 요소입니다. 이러한 결과는 미래 핵융합로의 플라즈마 제어 기술 확립에 기여할 것입니다. 팀의 보고서는 Physical Review Letters 에서 온라인으로 제공되었습니다 . 국제협력을 통해 프랑스에서 세계 최대 실험용 핵융합로인 ITER 건설이 진행 중이다.
-ITER에서는 수소 동위 원소 플라즈마의 "연소 상태"를 1억도 이상으로 유지하여 500MW 핵융합 에너지를 생성하는 실험이 수행됩니다. 이러한 실험의 성공에 대한 주요 장애물 중 하나는 자기유체역학적 불안정성으로 인해 플라즈마 붕괴를 제한하는 데 사용되는 자기장 구성이 발생하는 동안 "파열"이라고 하는 현상입니다.
중단으로 인해 고온 플라즈마가 용기의 내부 표면으로 흐르게 되어 구조적 손상이 발생하여 실험 일정이 지연되고 비용이 높아질 수 있습니다. 기계 및 ITER의 작동 조건은 중단을 방지하도록 신중하게 설계되었지만 불확실성이 남아 있으며 안전 장치로 전용 기계 보호 전략이 필요하도록 많은 실험을 수행합니다. 이 문제에 대한 유망한 해결책은 중단을 일으킬 수 있는 불안정의 첫 번째 징후가 감지되는 단계에서 플라즈마를 강제로 냉각시켜 플라즈마 대면 재료 구성 요소의 손상을 방지하는 "붕괴 완화"라는 기술입니다. 기본 전략으로 연구자들은 10켈빈 이하의 온도에서 동결된 수소의 얼음 알갱이를 사용하여 고온 플라즈마에 주입하는 방법을 개발하고 있습니다.
주입된 얼음은 표면에서 녹고 주변의 고온 플라즈마에 의한 가열로 인해 증발 및 이온화되어 얼음 주위에 저온, 고밀도 플라즈마(이하 "플라스모이드"라고 함) 층을 형성합니다. 이러한 저온, 고밀도 플라스모이드가 메인 플라즈마와 혼합되며, 그 과정에서 온도가 낮아집니다. 그러나 최근 실험에서 순수한 수소 얼음을 사용하면 플라스모이드가 목표 플라즈마와 섞이기 전에 방출되어 표면 아래 더 깊은 곳에서 고온 플라즈마를 냉각시키는 데 효과적이지 않다는 것이 분명해졌습니다. 이 방출은 플라스모이드의 높은 압력 때문이었습니다.
-질적으로 도넛 모양의 자기장에 갇힌 플라즈마는 압력에 비례하여 바깥쪽으로 팽창하는 경향이 있습니다. 수소 얼음이 녹고 이온화되어 형성되는 플라스모이드는 차갑지만 밀도가 매우 높습니다. 온도 평형이 밀도 평형보다 훨씬 빠르기 때문에 플라스모이드 압력은 뜨거운 대상 플라즈마의 압력보다 높아집니다. 그 결과 플라스모이드가 분극화되고 자기장을 가로질러 드리프트 동작을 경험하여 뜨거운 타겟 플라즈마와 완전히 혼합되기 전에 외부로 전파됩니다. 이 문제에 대한 해결책은 이론적 분석 에서 제안되었습니다 .
-모델 계산은 소량의 네온을 수소에 혼합함으로써 플라스모이드의 압력을 감소시킬 수 있다고 예측했습니다. 네온은 약 20켈빈의 온도에서 얼고 플라스모이드에서 강한 선 방사선을 생성합니다. 따라서 네온을 주입하기 전에 수소 얼음과 혼합하면 가열 에너지의 일부가 광자 에너지로 방출될 수 있습니다. 이러한 수소-네온 혼합물 사용의 유익한 효과를 입증하기 위해 일본 Toki에 위치한 LHD(Large Helical Device)에서 일련의 실험을 수행했습니다.
수년 동안 LHD는 직경 약 3mm의 얼음 펠릿을 1100m/s의 속도로 주입하는 "고체 수소 펠릿 주입기"라는 신뢰성 높은 장치를 운영해 왔습니다. 시스템의 높은 신뢰성으로 인해 플라즈마에 수소 얼음을 1ms의 시간 정밀도로 주입할 수 있어 주입된 얼음이 녹은 직후 플라즈마 온도와 밀도를 측정할 수 있습니다. 최근에는 새로운 레이저 기술을 사용하는 LHD 시스템에서 20kHz의 Thomson Scattering(TS)에 대한 세계 최고의 시간 분해능을 달성했습니다.
이 시스템을 사용하여 연구팀은 플라스모이드의 진화를 포착했습니다. 그들은 이론적인 계산에 의해 예측된 바와 같이 순수한 수소 얼음이 주입된 경우와 완전히 대조적으로 수소 얼음에 약 5%의 네온이 도핑되었을 때 플라스모이드 방출이 억제되었음을 발견했습니다. 또한, 실험은 네온이 플라즈마의 효과적인 냉각에 유용한 역할을 한다는 것을 확인했습니다. 이번 연구 결과는 고온 플라즈마에 소량의 네온이 도핑된 수소 얼음 알갱이를 주입하는 것이 플라스모이드 방출을 억제 해 플라즈마 의 심부 코어 영역을 효과적으로 냉각시키는데 유용하다는 것을 처음으로 보여주었다.
네온 도핑의 이러한 효과는 새로운 실험 현상으로서 흥미로울 뿐만 아니라 ITER에서 중단 완화의 기본 전략 개발을 지원합니다. ITER 중단 완화 시스템의 설계 검토는 2023년으로 예정되어 있으며 현재 결과는 시스템의 성능을 개선하는 데 도움이 될 것입니다.
추가 정보: A. Matsuyama et al, 혼합 H2+Ne 펠릿 주입을 사용한 환상형 플라즈마의 향상된 재료 동화 및 ITER에 대한 영향, 물리적 검토 편지 (2022). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.255001 저널 정보: Physical Review Letters 국립자연과학원 제공
https://phys.org/news/2023-01-cooling-million-degree-plasma-hydrogen-neon.html
======================
메모 2301070555 나의 사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
핵융합로의 토카막내부는 헬륨 비등점 4.22k을 이용한 1억도 이상으로 유지하여 500MW 핵융합 에너지를 생성하는 이온 플라즈마 상태이다. 유사시 안전장치로 냉각기의 작동이 제대로 이뤄지려면 1억도를 급냉시킬 냉매제가 필요한 상황이다.
연구결과 이 핵융합 반응에는 원자의 10 keV의 이상의 운동에너지가 필요하며 이 에너지는 중수소 원자가 약 1,000 km/sec의 속도로 충돌하는 것과 같다. 두 원자핵의 융합 반응이 일어나면 무거운 헬륨원자와 중성자가 하나씩 생기고 반응 전후의 질량 차이에 의해 에너지가 발생하는데(아인슈탄인의 E=Δmc2) 바로 핵융합 에너지이다. 에너지는 두입 자 헬륨원자(3.5 MeV)와 중성자(14.1 Mev)의 운동에너지로 발생된다. 두 입자의 운동에너지는 이어지는 다른 반응을 통해 빛 에너지나 열에너지의 형태로 변환되어 이용된다.
비등점이 가장낮은 헬륨이 중수소,삼중수소의 핵융합의 과정에서 사용되므로 이들이 만들어내는 1억이상의 토카막의 안전장치 냉매제는 헬륨의 다음의 비등점을 가진 네온이나 수소가 적합하다.
물론 향후 수백만MW 대규모 토카막 시설을 관리하려면 냉매제로 활용될 헬륨 다음의 최저저점 네온의 비등점 20.28켈빈이나 수소의 비등점27.07켈빈에 대한 확실한 매카니즘이 확립되어야 한다.
이에 모델 계산은 소량의 네온을 수소에 혼합함으로써 플라스모이드의 압력을 감소시킬 수 있다고 예측했다. 일종에 샘플b.qoms의 a+b=c 중첩.특이점 혼합방식이다. 여기서 a내온 소량<b수소 비율이다. 네온은 약 20켈빈의 온도에서 얼고 플라스모이드에서 강한 선 방사선을 생성한다. 따라서 네온을 주입하기 전에 수소 얼음과 혼합하면 가열 에너지의 일부가 광자 에너지로 방출될 수 있다.
기본 전략으로 연구자들은 10켈빈 이하의 온도에서 동결된 수소의 얼음 알갱이를 사용하여 고온 플라즈마에 주입하는 방법을 개발하고 있다. a(네온의 비등점 20.28켈빈)<+b(수소의 비등점27.07켈빈)===>10켈빈이가 가능하려면 샘플b.qoms()정의역 개념이 필수이다. 허허.
물론 또다른 방법은 샘플a.omsful.banq.vix.a 남게 하는 비법이다. 어휴!소설을 쓴다 써..! 빅뱅사건이후 우주가 급냉된 방식이다. 허허.
1억도이상을 비상시, 급냉시키려면 주입된 얼음은 표면에서 녹고 주변의 고온 플라즈마에 의한 가열로 인해 증발 및 이온화되어 얼음 주위에 저온, 고밀도 플라즈마(이하 "플라스모이드"라고 함) 층을 형성케 해야한다. 이러한 저온, 고밀도 플라스모이드가 메인 플라즈마와 혼합되며, 그 과정에서 온도가 낮아진다.
샘플 a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플 b. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
샘플 b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
샘플 c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca


Now, a team of Japanese researchers at the National Institute of Quantum Science and Technology (QST) and the National Institute of Fusion Science (NIFS) at the National Institute of Science and Technology (NINS) have added about 5% neon to hydrogen ice pellets, which is more than when pure hydrogen ice pellets are injected. It can cool the plasma deeper below the surface and therefore more effectively.
Researchers use experimental measurements with theoretical models and advanced diagnostics in the NIFS-owned Large Helical Device to elucidate the dynamics of dense plasmoids that form around ice pellets and identify the physical mechanisms responsible for the successful performance enhancement of forced cooling systems. I did.
It is indispensable for conducting experiments in ITER. These results will contribute to the establishment of plasma control technology for future nuclear fusion reactors. The team's report is available online at Physical Review Letters. Through international cooperation, construction of the world's largest experimental nuclear fusion reactor, ITER, is underway in France.
-In ITER, experiments are conducted to generate 500 MW of fusion energy by maintaining the "burning state" of a hydrogen isotope plasma above 100 million degrees. One of the major obstacles to the success of these experiments is a phenomenon called "rupture" during which magnetohydrodynamic instability causes the magnetic field configuration used to limit plasma decay.
- Plasma trapped in a qualitatively donut-shaped magnetic field tends to expand outward in proportion to the pressure. Formed from melting and ionizing hydrogen ice, plasmoids are cold but very dense. Because temperature equilibrium is much faster than density equilibrium, the plasmoid pressure rises above that of the hot target plasma. As a result, the plasmoid becomes polarized and experiences a drift motion across the magnetic field, propagating outward before fully mixing with the hot target plasma. A solution to this problem has been proposed in a theoretical analysis.
- Model calculations predicted that the pressure of the plasmoid could be reduced by mixing small amounts of neon into hydrogen. Neon freezes at a temperature of about 20 Kelvin and produces intense line radiation from plasmoids. So, if neon is mixed with hydrogen ice before implantation, some of the heating energy can be released as photon energy. To demonstrate the beneficial effects of using these hydrogen-neon mixtures, a series of experiments were conducted at the Large Helical Device (LHD) located in Toki, Japan.
Note 1.
Numerous stars such as the sun (恒星, built-in stars) have nuclei of light elements such as hydrogen (1H), deuterium (2H or 2D), tritium (3H or 3T), helium (4He, lithium (6Li)) under ultrahigh temperature and high pressure. Light is emitted through the combined nuclear fusion reaction.
2D+3T→4He+1n+17.6 MeV
When deuterium and tritium atoms come close to each other, a force (repulsion) acts to repel each other due to the electrostatic force between two objects with the same positive charge. In order for the fusion reaction of these two atomic nuclei to occur, high energy exceeding this repulsive force is required. As a result of the research, this nuclear fusion reaction requires more than 10 keV of kinetic energy of atoms, and this energy is equivalent to that of deuterium atoms colliding at a speed of about 1,000 km/sec. When the fusion reaction of two atomic nuclei occurs, one heavy helium atom and one neutron are produced, and energy is generated by the mass difference before and after the reaction (E=Δmc2 of Einstein), which is nuclear fusion energy. Energy is generated by the kinetic energy of two particles helium atoms (3.5 MeV) and neutrons (14.1 Mev). The kinetic energy of the two particles is converted into light energy or thermal energy through subsequent reactions and used.
======================
memo 2301070555 my thought experiment oms storytelling
The inside of the tokamak of the nuclear fusion reactor is in an ion plasma state that generates 500MW of nuclear fusion energy by maintaining it at 100 million degrees or more using a helium boiling point of 4.22k. As a safety device in case of emergency, in order for the cooler to work properly, a refrigerant that can rapidly cool 100 million degrees is required.
As a result of the research, this nuclear fusion reaction requires more than 10 keV of kinetic energy of atoms, and this energy is equivalent to that of deuterium atoms colliding at a speed of about 1,000 km/sec. When the fusion reaction of two atomic nuclei occurs, one heavy helium atom and one neutron are produced, and energy is generated by the mass difference before and after the reaction (E=Δmc2 of Einstein), which is nuclear fusion energy. Energy is generated by the kinetic energy of two particles helium atoms (3.5 MeV) and neutrons (14.1 Mev). The kinetic energy of the two particles is converted into light energy or thermal energy through subsequent reactions and used.
Since helium with the lowest boiling point is used in the process of nuclear fusion of deuterium and tritium, neon or hydrogen with the boiling point next to helium is suitable as a safety device refrigerant for over 100 million tokamak produced by them.
Of course, to manage large-scale tokamak facilities of millions of MW in the future, a clear mechanism for the boiling point of 20.28 Kelvin of neon or 27.07 Kelvin of hydrogen, the lowest point next to helium to be used as a refrigerant, must be established.
Model calculations predicted that the pressure of the plasmoid could be reduced by mixing a small amount of neon into the hydrogen. A+b=c superimposition of sample b.qoms in a kind. It is a singularity mixing method. where a is the small amount produced <b the hydrogen ratio. Neon freezes at a temperature of about 20 Kelvin and produces intense line radiation from plasmoids. Therefore, if neon is mixed with hydrogen ice before implantation, some of the heating energy can be released as photon energy.
As a basic strategy, the researchers are developing a way to inject into a high-temperature plasma using ice pellets of hydrogen frozen at temperatures below 10 Kelvin. a (neon boiling point 20.28 Kelvin) <+b (hydrogen boiling point 27.07 Kelvin) ===> 10 Kelvin For this to be possible, the sample b.qoms() domain concept is essential. haha.
Another way, of course, is to keep the sample a.omsful.banq.vix.a. Ugh! I write a novel..! This is how the universe cooled rapidly after the Big Bang event. haha.
In case of emergency, rapid cooling of more than 100 million degrees, the injected ice melts on the surface and evaporates and ionizes due to heating by the surrounding high-temperature plasma to form a low-temperature, high-density plasma (hereinafter referred to as "plasmoid") layer around the ice. should be ke These low-temperature, high-density plasmoids are mixed with the main plasma, and the temperature is lowered in the process.
Sample a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample b. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

.Physicists find that organelles grow in random bursts
물리학자들은 소기관이 무작위로 폭발적으로 성장한다는 사실을 발견했습니다

Talia Ogliore, 워싱턴 대학교 세인트루이스 세인트루이스에 있는 워싱턴 대학의 연구에 따르면 진핵 세포의 소기관은 빌딩 블록의 제한된 풀에서 무작위로 폭발적으로 성장합니다. 신용: 셔터스톡 JANUARY 6, 2023
-모든 동물, 식물 및 균류를 포함하여 우리가 알고 있는 대부분의 생명을 구성하는 진핵 세포는 고도로 구조화된 개체입니다. 이 세포들은 유전 정보 를 저장하는 핵 또는 화학 에너지를 생산하는 미토콘드리아 와 같은 막으로 둘러싸인 소기관과 같은 더 작은 내부 비트를 조립하고 유지합니다 .
-그러나 그들이 이러한 공간적 구획으로 스스로를 조직하는 방법에 대해 많은 것을 배워야 합니다. 세인트루이스에 있는 워싱턴 대학의 물리학자들은 진핵 세포 가 소기관 크기의 평균 변동을 강력하게 제어할 수 있음을 보여주는 새로운 실험을 수행했습니다.
-소기관 크기가 과학자들이 이론적으로 예측하는 보편적인 확장 관계를 따른다는 것을 입증함으로써 그들의 새로운 프레임워크는 소기관이 빌딩 블록의 제한된 풀에서 무작위로 폭발적으로 성장한다는 것을 암시합니다.
이 연구는 1월 6일 Physical Review Letters 에 게재 되었습니다. "우리 연구에서, 우리는 질서정연한 '벽돌 하나하나' 조립과는 거리가 먼 소기관이 성장하는 단계가 확률론적 폭발에서 발생한다고 제안했습니다. Mukherji는 "이러한 폭발은 소기관 크기가 제어되는 정밀도를 근본적으로 제한하지만 좁은 창 내에서 소기관 크기의 노이즈를 유지합니다."라고 말했습니다. "폭발적인 성장은 세포가 평균적으로 신뢰할 수 있지만 플라스틱 소기관 크기를 유지할 수 있는 일반적인 생물물리학적 메커니즘을 제공합니다." 소기관은 환경 요구에 따라 세포가 성장하거나 축소될 수 있도록 충분히 유연해야 합니다. 그러나 소기관의 크기는 일정한 한계 내에서 유지되어야 합니다. 생물학자들은 이전에 소기관 크기를 조절하는 특정 분자 요인을 확인했지만 이 연구는 소기관 크기 제어의 기본이 되는 정량적 원칙에 대한 새로운 통찰력을 제공합니다. 이 연구에서는 발아 효모를 모델 유기체 로 사용했지만 팀은 이러한 조립 메커니즘이 다양한 종과 세포 유형 에 걸쳐 어떻게 활용되는지 탐구하게 되어 기쁩니다 . Mukherji는 이러한 견고성 패턴이 생명공학 응용을 위해 소기관 어셈블리를 활용하는 방법과 질병의 맥락에서 소기관 생물 발생의 결함을 발견하는 방법에 대해 우리에게 무엇을 가르쳐줄 수 있는지 조사할 계획이라고 말했습니다. Mukherji는 "소기관 크기 견고성의 패턴은 발아 효모와 인간 iPS 세포 간에 공유됩니다."라고 말했습니다. "이러한 폭발을 일으키는 근본적인 분자 메커니즘은 아직 완전히 밝혀지지 않았으며 소기관 에 따라 다르며 잠재적으로 종에 따라 다를 수 있습니다." 추가 정보: Kiandokht Panjtan Amiri 외, Organelle 크기 제어의 견고성과 보편성, Physical Review Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.018401 저널 정보: Physical Review Letters 세인트루이스 워싱턴 대학교 제공
https://phys.org/news/2023-01-physicists-organelles-random.html
===========================
메모 2301070700나의 사고실험 oms 스토리텔링
물리학자들은 소기관이 무작위로 폭발적으로 성장한다는 사실을 발견했다. 이렇듯 폭발적인 소기관이 빌딩 블록의 제한된 풀에서 무작위로 '폭발적으로 성장한다'는 것은 암호화된 샘플c.oss.cell의 인터페이스가 '열려진 상태로 확산되고 있다'는 것이다. 허허.
샘플 a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플 b. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
샘플 b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
샘플 c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

-Eukaryotic cells, which make up most of life as we know it, including all animals, plants, and fungi, are highly structured entities. These cells assemble and maintain smaller internal bits, such as membrane-enclosed organelles, such as nuclei that store genetic information or mitochondria that produce chemical energy.
-But there's a lot to be learned about how they organize themselves into these spatial compartments. Physicists at Washington University in St. Louis conducted a new experiment showing that eukaryotic cells can strongly control the average fluctuations in organelle size.
-By demonstrating that organelle size follows the universal scaling relationship that scientists theoretically predict, their new framework suggests that organelles grow randomly and explosively from a limited pool of building blocks.
===========================
memo 2301070700 my thought experiment oms storytelling
Physicists have discovered that organelles grow randomly and explosively. This 'explosive growth' of these explosive organelles randomly from a limited pool of building blocks means that the interfaces of the encrypted sample c.oss.cell are 'spreading open'. haha.
Sample a.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample b. qoms (standard)
0000000011=2,0
0000001100
0000001100
0000010010
0001100000
0101000000
0010010000
0100100000
2000000000
0010000001
sample b.poms (standard)
q0000000000
00q00000000
0000q000000
000000q0000
00000000q00
0000000000q
0q000000000
000q0000000
00000q00000
0000000q000
000000000q0
sample c.oss (standard)
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca
댓글