.New Supercomputer Simulations Provide Clue to Missing Planets Mystery
http://blog.naver.com/mssoms
http://jl0620.blogspot.com
http://jk0620.tripod.com
https://www.facebook.com/junggoo.lee.9

.New Supercomputer Simulations Provide Clue to Missing Planets Mystery
새로운 슈퍼컴퓨터 시뮬레이션은 행성 미스터리 실종에 대한 단서를 제공합니다
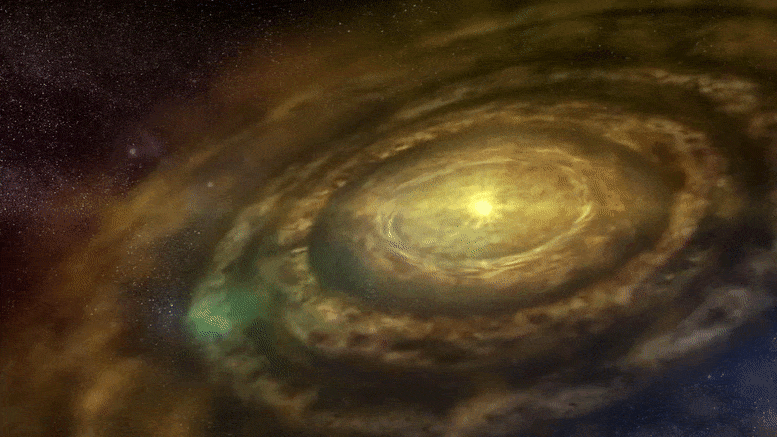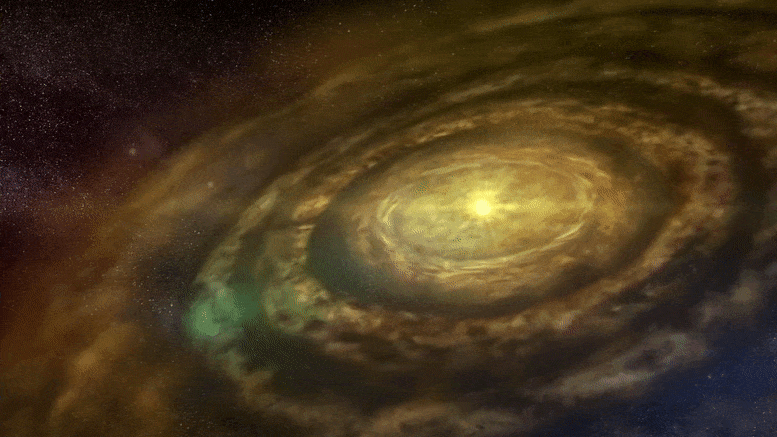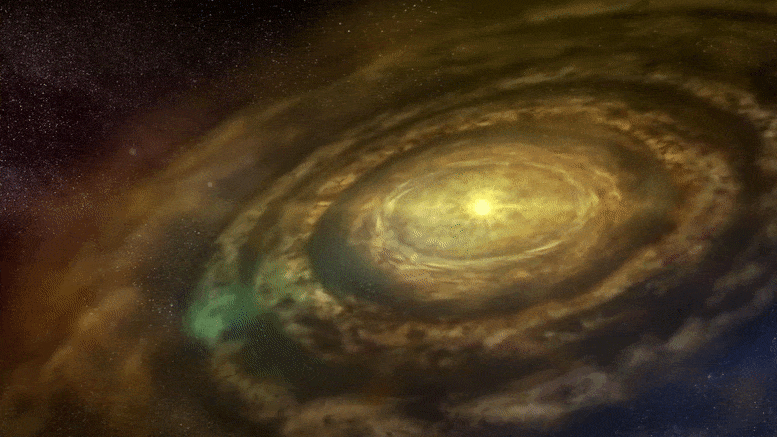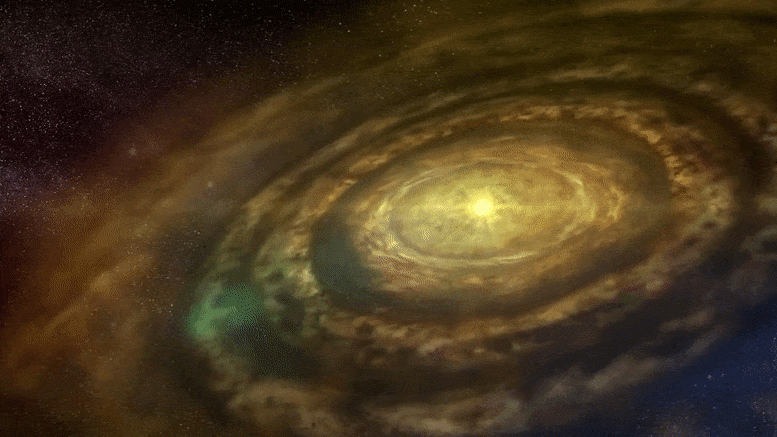
주제:천문학천체물리학국립 자연 과학 연구소행성인기있는 으로 자연 과학의 국립 연구소 , 2021 11월 14일 원시 행성 디스크 애니메이션 행성 형성은 젊은 별 주위의 가스와 먼지 원반에서 관찰되는 고리와 틈에 대한 가능한 설명 중 하나입니다. 그러나 이 이론은 고리와 관련된 행성을 찾는 것이 드문 이유를 설명하는 데 어려움이 있습니다. 새로운 슈퍼컴퓨터 시뮬레이션은 고리를 생성한 후 행성이 멀어져 고리를 남길 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 이것은 고리 형성에 대한 행성 이론을 강화할 뿐만 아니라 시뮬레이션은 이동하는 행성이 디스크에서 실제로 관찰된 것과 일치하는 다양한 패턴을 생성할 수 있음을 보여줍니다.
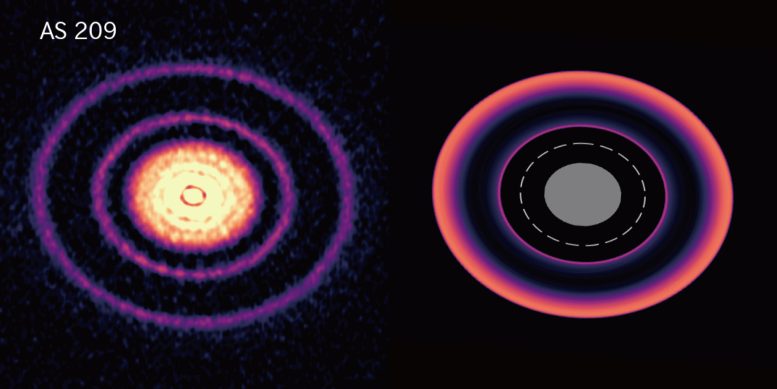
원시 행성 디스크 비교 ALMA가 관측한 원시행성 원반(왼쪽)과 ATERUI II 시뮬레이션에서 얻은 행성 이동 중 원시행성 원반(오른쪽). 시뮬레이션에서 점선은 행성의 궤도를 나타내며 회색 영역은 시뮬레이션의 계산 영역에 포함되지 않는 영역을 나타냅니다. 크레딧: Kazuhiro Kanagawa, ALMA(ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
-어린 별들은 가스와 먼지로 이루어진 원시행성 원반으로 둘러싸여 있습니다. 세계에서 가장 강력한 전파 망원경 배열 중 하나인 ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array)는 이러한 원시행성 디스크에서 더 조밀하고 덜 조밀한 고리와 틈의 다양한 패턴을 관찰했습니다. 디스크에서 형성되는 행성의 중력 효과는 이러한 구조를 설명하는 하나의 이론이지만 고리 근처의 행성을 찾는 후속 관측은 대체로 성공적이지 못했습니다. 이 연구에서 일본 이바라키 대학, 고가쿠인 대학, 도호쿠 대학의 팀은 일본 국립 천문대의 세계에서 가장 강력한 천문학 전용 슈퍼컴퓨터인 ATERUI II를 사용하여 행성이 초기 형성에서 멀어지는 경우를 시뮬레이션했습니다. 대지. 그들의 결과는 저점도 원반에서 행성이 안쪽으로 이동할 때 행성의 초기 위치에 형성된 고리가 움직이지 않는다는 것을 보여주었습니다. 팀은 세 가지 다른 단계를 식별했습니다. 1단계에서 행성이 안쪽으로 이동할 때 초기 고리는 그대로 유지됩니다. 2단계에서 초기 고리가 변형되기 시작하고 두 번째 고리가 행성의 새로운 위치에서 형성되기 시작합니다. 3단계에서는 초기 링이 사라지고 후자의 링만 남습니다.
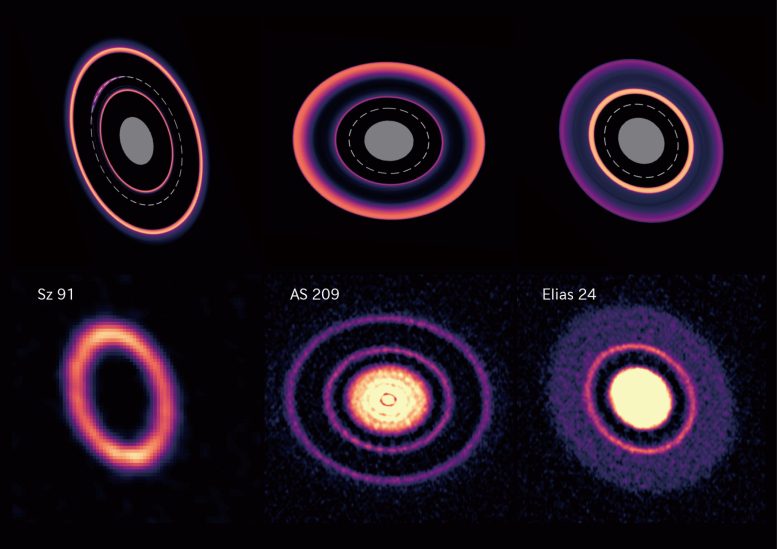
링 형성과 변형의 3단계 ATERUI II(위)의 시뮬레이션에서 발견된 링 형성 및 변형의 세 단계를 ALMA(아래)에서 관찰한 실제 예와 비교합니다. 시뮬레이션에서 점선은 행성의 궤도를 나타내고 회색 영역은 시뮬레이션의 계산 영역에서 다루지 않는 영역을 나타냅니다. 위쪽 행에서 시뮬레이션된 원시행성 원반은 행성 이동이 시작될 때(단계 I), 행성 이동 중에(단계 II), 행성 이동이 끝날 때(단계 III) 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 표시됩니다. 크레딧: Kazuhiro Kanagawa, ALMA(ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
이러한 결과는 외륜 근처에서 행성이 거의 관찰되지 않는 이유를 설명하는 데 도움이 되며 시뮬레이션에서 확인된 세 단계는 실제 고리에서 관찰된 패턴과 잘 일치합니다. 중심 별에 가까운 행성을 더 잘 검색할 수 있는 차세대 망원경의 고해상도 관측은 이러한 시뮬레이션이 현실과 얼마나 잘 일치하는지 결정하는 데 도움이 될 것입니다.
참조: 2021년 11월 12일 The Astrophysical Journal , Kazuhiro D. Kanagawa, Takayuki Muto 및 Hidekazu Tanaka의 "원행성 원반에서 행성 형성의 발자국으로서의 먼지 고리" . DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac282b
https://scitechdaily.com/new-supercomputer-simulations-provide-clue-to-missing-planets-mystery/
====================
메모 2111171916 나의 사고실험 oms스토리텔링
별 주위에 실종된 행성을 찾고자 한다면 별이 가질 수 있는 본래의 원반 크기의 궤도를 알아야내야 한다. 이를 vixer시스템으로 본다. 샘플1.oms을 항성의 원시원반 모드로 드려다 볼 필요가 있다. 시스템 a의 정식명칭은 system a'7/b1g3k3n6o5이다. 이것이 베이스 vix_a이다.
vix_a을 항성이라 가정할 때, mser 섹터의 항성부a'7/ 행성부b1g3k3n6o5 이다. 소실된 행성이 무엇인지 근본적으로 알아낼 수 있다. 허허.
샘플1.oms(standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플2. oss
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

-Young stars are surrounded by a protoplanetary disk of gas and dust. The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), one of the most powerful radio telescope arrays in the world, has observed various patterns of denser and less dense rings and fissures in these protoplanetary disks. The gravitational effect of planets forming on disks is one theory explaining these structures, but subsequent observations of planets near the rings have largely been unsuccessful. In this study, a team from Japan's Ibaraki University, Kogakuin University, and Tohoku University used the ATERUI II, the world's most powerful astronomy-only supercomputer, from the National Observatory of Japan to simulate when a planet moves away from its initial formation. Earth. Their results showed that the rings formed in the planet's initial positions do not move as the planet moves inward in the low-viscosity disk. The team identified three different stages. When the planet moves inward in Phase 1, the initial rings remain the same. In stage 2, the initial rings begin to transform and the second rings begin to form at their new location on the planet. In step 3, the initial ring disappears, leaving only the latter ring.
======================
Memo 2111171916 My thought experiment oms storytelling
If you want to find a missing planet around a star, you need to know the original disk-sized orbit that the star can have. We see this as a vixer system. You need to look at sample 1.oms in stellar protodisk mode. The official name of system a is system a'7/b1g3k3n6o5. This is the base vix_a.
Assuming vix_a is a star, it is the stellar part a'7/planetary part b1g3k3n6o5 of the mser sector. We can fundamentally find out what the lost planet is. haha.
Sample 1.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample 2. oss
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

.Neutron Crystallography Takes a Deep Dive Into Water Networks Surrounding DNA
중성자 결정학은 DNA를 둘러싼 물 네트워크에 대해 자세히 설명합니다
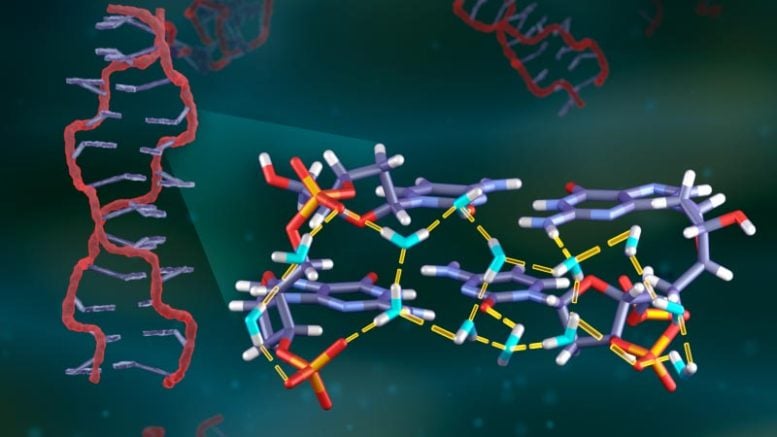
주제:생화학통풍하다분자 생물학국립 보건원오크리지 국립연구소물 으로 오크 리지 국립 연구소 , 2021 11월 17일 물 분자와 DNA 사이의 수소 결합 패턴 Vanderbilt University 연구원들은 ORNL에서 중성자를 사용하여 물 분자(파란색으로 표시)와 DNA 사이의 수소 결합 패턴을 밝혔습니다. 이번 발견은 물이 DNA 기능에 미치는 영향에 대한 통찰력을 제공하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 크레딧: ORNL/Jill Hemman SCIENCE NOVEMBER 17, 2021
물은 인체 내에서 몇 가지 중요한 역할을 하며 세포 의 DNA 에도 영향을 미칩니다 . DNA 이중 나선의 전체 표면은 물 분자 층으로 코팅되어 있습니다. 이 물막은 분자 사이에 수소 원자를 공유하여 만들어진 수소 결합을 통해 유전 물질에 부착됩니다. 수소 결합을 통해 물은 DNA가 어떻게 형성되고 다른 분자와 상호 작용하는지에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 어떤 경우에는 물이 단백질이 DNA 서열을 인식하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
과학자들은 수소 결합이 일어나는 위치와 수소 원자가 공유되는 방식을 추정할 수 있지만 실험적 증거를 수집하는 것은 어렵습니다. Vanderbilt University가 이끄는 연구팀은 DNA 주변의 물의 수소 결합 패턴에 대한 가장 상세한 보기를 성공적으로 포착한 방법을 사용하여 물이 DNA 기능에 미치는 영향을 연구하는 새로운 가능성을 열었습니다.
방법론과 에너지부(DOE) 오크리지 국립연구소(ORNL)의 중성자 산란을 통해 부분적으로 생성된 결과에 대한 자세한 내용은 핵산 연구 저널에 게재되었습니다 . “물은 매우 특정한 상호작용에 대해서도 DNA와 다른 분자 사이의 매개체 역할을 합니다. 분자가 DNA의 한 부분에 결합하려면 먼저 이 물 껍질을 통과해야 합니다.”라고 Vanderbilt 대학의 생화학 교수이자 연구 교신 저자인 Martin Egli가 말했습니다.
-"DNA 과정에 대한 이해를 높이려면 주변 물이 무엇을 하고 분자 주위에 어떻게 배열되는지 정확히 아는 것이 중요합니다." X선 회절 실험은 물 분자가 DNA 주변에 위치하는 위치를 밝혀냈지만 이들 분자 사이의 수소 결합 패턴은 여전히 숨겨져 있었습니다. 반면에 중성자는 물의 수소 원자와 같은 가벼운 요소에 더 민감하여 연구자가 수소 결합이 발생하는 위치와 생성되는 분자를 결정할 수 있습니다. “X-선으로 물 분자에 대해 얻을 수 있는 일반적인 전자 밀도는 축구공과 같은 구체입니다.
-수소 원자를 볼 수 없기 때문에 분자에는 방향성이 없습니다.”라고 이 연구에 참여한 ORNL 과학자인 Leighton Coates가 말했습니다. "반면 중성자를 사용하면 물 분자가 부메랑처럼 보입니다. 수소가 어떻게 배향되고 수소 결합 패턴을 결정하는지 볼 수 있습니다.” 이 연구를 수행하기 위해 팀은 시토신과 구아닌을 번갈아 가며 6개의 염기쌍을 가진 잘 연구된 DNA 단편의 결정화된 샘플을 사용했습니다.
d(CGCGCG)로 알려진 이 단편은 1979년에 결정 구조가 결정된 최초의 DNA 서열이었습니다. 과학자들은 중수소 산화물 용액을 사용하여 단편에 있는 많은 수소 원자를 중수소 원자로 대체했습니다. 수소의 동위 원소인 중수소는 수소와 비교하여 중성자에 의해 다르게 “보이기” 때문에 연구자들은 중수소를 사용하여 DNA와 물 구조에 대한 정보를 선택적으로 수집할 수 있습니다.
연구팀은 ORNL의 Spallation Neutron Source(SNS)에서 거대분자 중성자 회절계(MaNDi)를 사용하여 이 조각에 대한 중성자 회절 데이터를 수집했습니다. 물의 움직임을 줄이기 위해 팀은 차가운 질소 가스를 사용하여 샘플을 100K(거의 -280°F)로 냉각했습니다. Egli는 "샘플에서 물의 이동성을 낮춤으로써 물 분자를 격자와 같은 배열로 유지할 수 있어 물 분자의 위치와 위치를 잠글 수 있습니다."라고 말했습니다. "실온에서 이 데이터를 수집하면 많은 물 분자의 위치가 기본적으로 번지고 우주의 다양한 위치에 분산됩니다." Vanderbilt 대학의 생화학 연구 조교수이자 연구 공동 저자인 Joel Harp는 "중성자를 사용하면 수소 결합의 수(예: 다중 결합 또는 단 하나)로 물 분자를 구별할 수도 있습니다.
밴더빌트 대학 구조 생물학 센터의 생체 분자 결정학 시설에서 유사한 결정에 대해 X선 회절 실험을 수행하여 물 분자의 산소 원자가 DNA 단편 주위에 위치하는 위치를 결정했습니다. 이러한 보완적인 기술을 결합하여 연구원들은 DNA 이중 나선 주위의 물 분자 방향에 대한 가장 상세한 분석을 달성했습니다. 그들은 DNA 조각과 직접 접촉하거나 근처에 있는 64개의 물 분자의 방향을 포착했습니다. 이 연구는 홈 내부와 당-인산염 백본 주변을 포함하여 DNA 구조의 두드러진 부분 내에서 물 분자가 수소 결합을 제공하거나 수용하는 방법을 보여주었습니다. 일부 수소 결합은 예상치 못한 것으로, 이전의 가정과 달리 이 방법이 DNA 물 네트워크에 대한 분자 역학 모델을 확인하는 데 도움이 될 수 있음을 보여줍니다.
연구팀은 현재 이 방법을 사용하여 물이 RNA 와 같은 다른 거대분자 주위에서 어떻게 거동하는지 연구하고 있습니다. "이제 우리가 배운 것을 더 도전적인 프로젝트에 적용할 때라고 생각합니다."라고 Egli가 말했습니다. “물은 생명의 가장 기본적인 존재이며, 아직 발견해야 할 것들이 많이 있습니다.”
참조: Joel M Harp, Leighton Coates, Brendan Sullivan 및 Martin Egli가 2021년 4월 19일 Nucleic Acids Research의 "저온 중성자 결정학으로 분석한 왼손잡이 Z-DNA 단편 주변의 물 구조" . DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab264 이 연구는 DOE Office of Science와 NIH(National Institutes of Health)의 지원을 받았습니다.
====================
메모 2111172028 나의 사고실험 oms스토리텔링
DNA 과정에 대한 이해를 높이려면 주변 물이 무엇을 하고 분자 주위에 어떻게 배열되는지 정확히 아는 것이 중요합니다. 물은 수소와 산소가 구체를 이룬 분자인데 방향성이 없는 분자를 중성자로 보면 수소가 어떻게 배향되고 수소 결합 패턴을 결정하는지 볼 수 있다고 한다.
이는 마치 샘플2.oss에서 베이스 마방진의 배열 스핀을 드려다보는 듯 할 것이다. 허허.
샘플1.oms(standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
샘플2. oss
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca

--"To better understand DNA processes, it's important to know exactly what the surrounding water does and how it is arranged around molecules." X-ray diffraction experiments revealed where water molecules were located around the DNA, but the pattern of hydrogen bonding between these molecules was still hidden. Neutrons, on the other hand, are more sensitive to light elements, such as the hydrogen atoms in water, allowing researchers to determine where hydrogen bonds occur and which molecules are formed. “The typical electron density you can get for a water molecule with X-rays is a soccer ball-like sphere.
-The molecule has no orientation because you can't see the hydrogen atoms," said ORNL scientist Leighton Coates, who was involved in the study. "With neutrons, on the other hand, water molecules look like a boomerang. You can see how the hydrogens are oriented and determine the hydrogen bonding pattern." To conduct this study, the team used a crystallized sample of a well-studied DNA fragment with six base pairs alternating between cytosine and guanine.
This fragment, known as -d (CGCGCG), was the first DNA sequence whose crystal structure was determined in 1979. Scientists used a solution of deuterium oxide to replace many of the hydrogen atoms in the fragments with deuterium atoms. Because deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen, is "looked up" differently by neutrons compared to hydrogen, researchers can use deuterium to selectively gather information about the structure of DNA and water.
-The research team collected neutron diffraction data for this fragment using a macromolecular neutron diffractometer (MaNDi) at ORNL's Spallation Neutron Source (SNS). To reduce water movement, the team used cold nitrogen gas to cool the sample to 100K (nearly -280°F). "By lowering the mobility of water in the sample, we can keep the water molecules in a lattice-like arrangement, which locks the position and position of the water molecules," Egli said. "Collecting this data at room temperature essentially smears the positions of many water molecules and disperses them in various locations in space." Joel Harp, assistant professor of biochemistry research at Vanderbilt University and research co-author Joel Harp, said, "Using neutrons, you can also differentiate water molecules by the number of hydrogen bonds (such as multiple bonds or just one).
======================
memo 2111172028 my thought experiment oms storytelling
To better understand DNA processes, it's important to know exactly what the surrounding water does and how it is arranged around molecules. Water is a molecule made up of hydrogen and oxygen, but it is said that if you look at a non-directional molecule as a neutron, you can see how the hydrogen is oriented and determines the hydrogen bonding pattern.
It would be like looking at the array spin of the base magic square in sample 2.oss. haha.
Sample 1.oms (standard)
b0acfd 0000e0
000ac0 f00bde
0c0fab 000e0d
e00d0c 0b0fa0
f000e0 b0dac0
d0f000 cae0b0
0b000f 0ead0c
0deb00 ac000f
ced0ba 00f000
a0b00e 0dc0f0
0ace00 df000b
0f00d0 e0bc0a
sample 2. oss
zxdxybzyz
zxdzxezxz
xxbyyxzzx
zybzzfxzy
cadccbcdc
cdbdcbdbb
xzezxdyyx
zxezybzyy
bddbcbdca
댓글